Background

In this challenge, you’ll learn the basic of reverse engineering and reading assembly code. Without further ado, let’s dive in.
Solution
First, I downloaded the downloadable file and unzip it.
After we unzipped the file, we have two file: wide, db.ex. wide is a 64-bit ELF executable, let’s see what it’s doing.
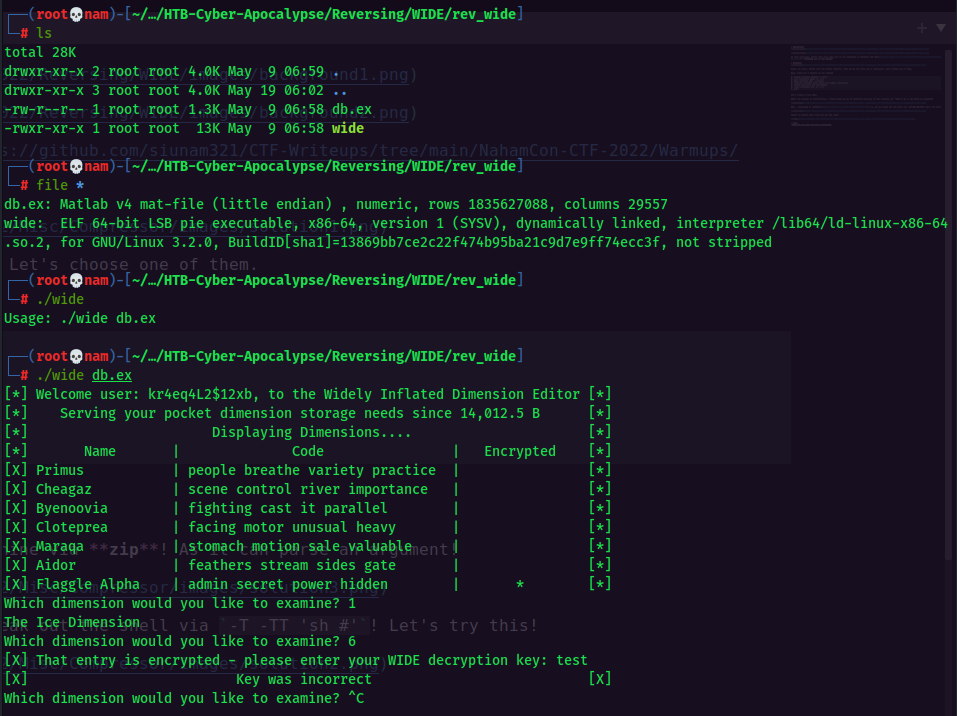
Looks like we need a decryption key to decrypt the Flaggle Alpha storage. Next, we can use any reverse engineering tools to disassembly that executable. Some folks might use Ghidra, IDA, GDB, and etc. I’ll use Cutter, as it’s beginner-friendly.
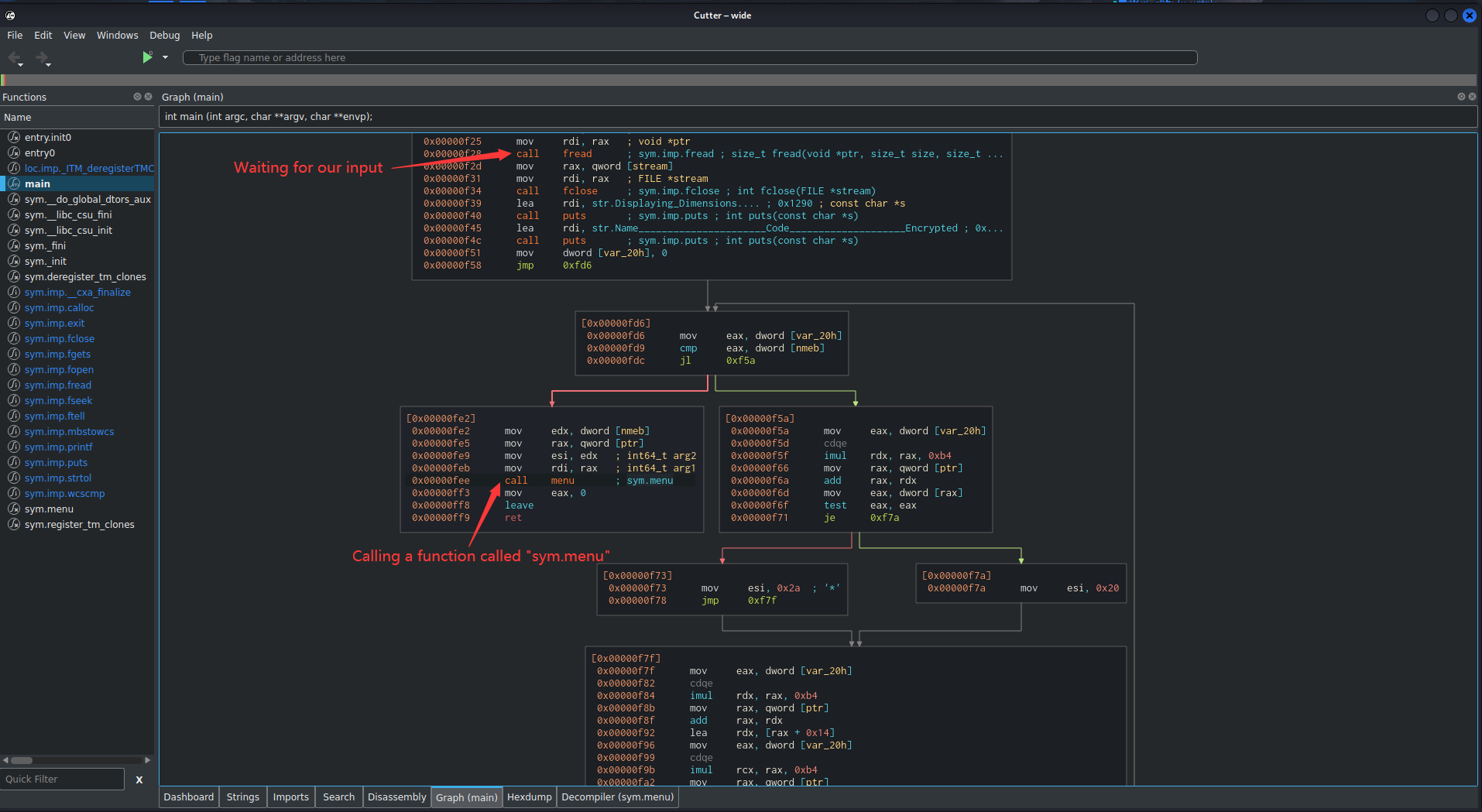
As you can see, in the main function, there is a 1 interesting call instruction to invoke a function called sym.menu, maybe it’s like checking our decryption key is correct or not?? Let’s check that out.
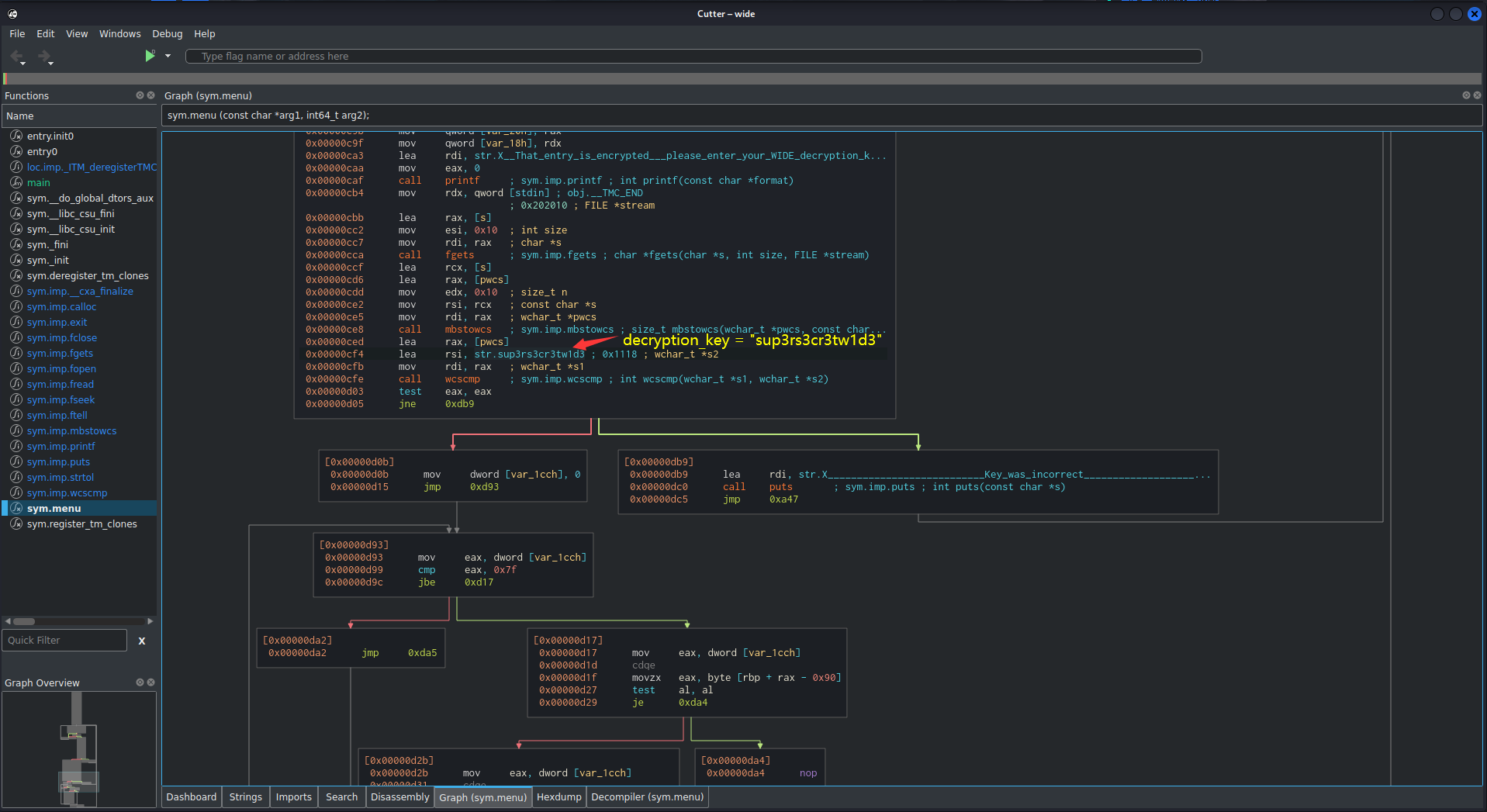
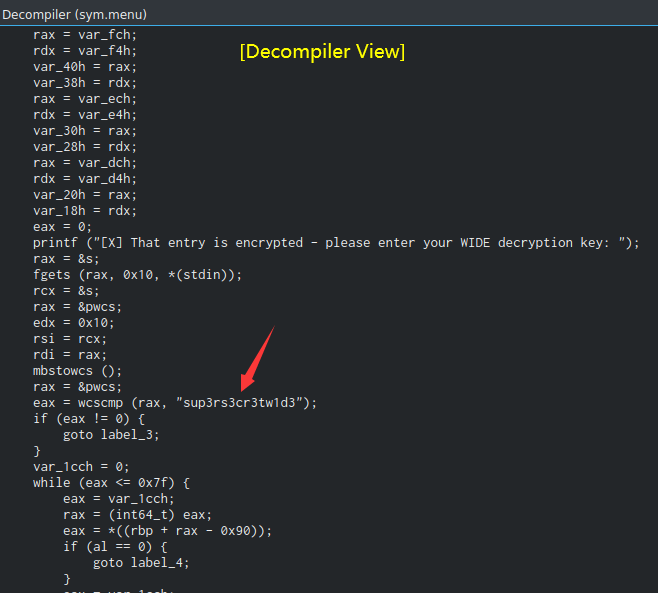
Hmm… We see a string that stores the decryption key: sup3rs3cr3tw1d3
Also, the wcscmp instruction is comparing our decryption key that we’re provided is matched to sup3rs3cr3tw1d3 or not. If it’s not matched, we’ll jump to 0x00000db9, which is the string of Key was incorrect. This is because it has a jne instruction, which is jump if not equal to.
Now, let’s use sup3rs3cr3tw1d3 decryption key to decrypt the Flaggle Alpha storage!
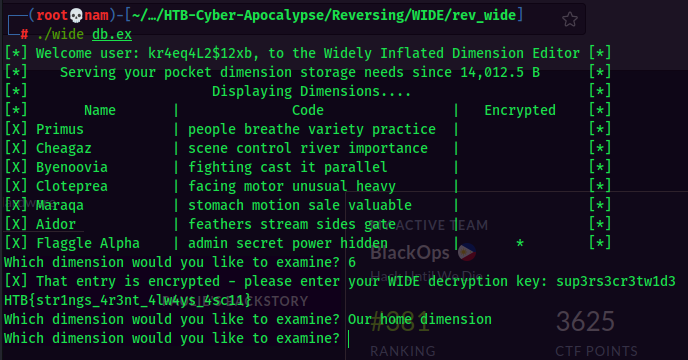
And here’s the flag!!
Flag
HTB{str1ngs_4r3nt_4lw4ys_4sc11}