Downgrade
Background
During recent auditing, we noticed that network authentication is not forced upon remote connections to our Windows 2012 server. That led us to investigate our system for suspicious logins further. Provided the server's event logs, can you find any suspicious successful login?
Difficulty: Medium
- Overall difficulty for me: Medium
In this challenge, you can spawn a docker instance and download a file:
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/HackTheBoo/Forensics/Downgrade]
└─# unzip forensics_downgrade.zip
Archive: forensics_downgrade.zip
inflating: Logs/Application.evtx
inflating: Logs/HardwareEvents.evtx
inflating: Logs/Internet Explorer.evtx
inflating: Logs/Key Management Service.evtx
inflating: Logs/Microsoft-Windows-ApplicationResourceManagementSystem%4Operational.evtx
inflating: Logs/Microsoft-Windows-AppModel-Runtime%4Admin.evtx
inflating: Logs/Microsoft-Windows-AppReadiness%4Admin.evtx
inflating: Logs/Microsoft-Windows-AppReadiness%4Operational.evtx
inflating: Logs/Microsoft-Windows-AppXDeployment%4Operational.evtx
[...]
Bunch of Windows Event Logs!
Find the flag
Question 1
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/HackTheBoo/Forensics/Downgrade]
└─# nc 161.35.164.157 31944
+-----------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| Title | Description |
+-----------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| Downgrade | During recent auditing, we noticed that |
| | network authentication is not forced upon remote |
| | connections to our Windows 2012 server. That |
| | led us to investigate our system for |
| | suspicious logins further. Provided the server's event |
| | logs, can you find any suspicious successful |
| | login? |
+-----------+---------------------------------------------------------+
Which event log contains information about logon and logoff events? (for example: Setup)
>
To inspect those logs, I'll fire up my Windows 10 Pro virtual machine, and transfer those logs:
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/HackTheBoo/Forensics/Downgrade]
└─# python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
PS C:\Users\Student\Desktop> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://192.168.183.141/forensics_downgrade.zip -OutFile forensics_downgrade.zip
In the Event Viewer, we can see that Security contains information about logon and logoff events:
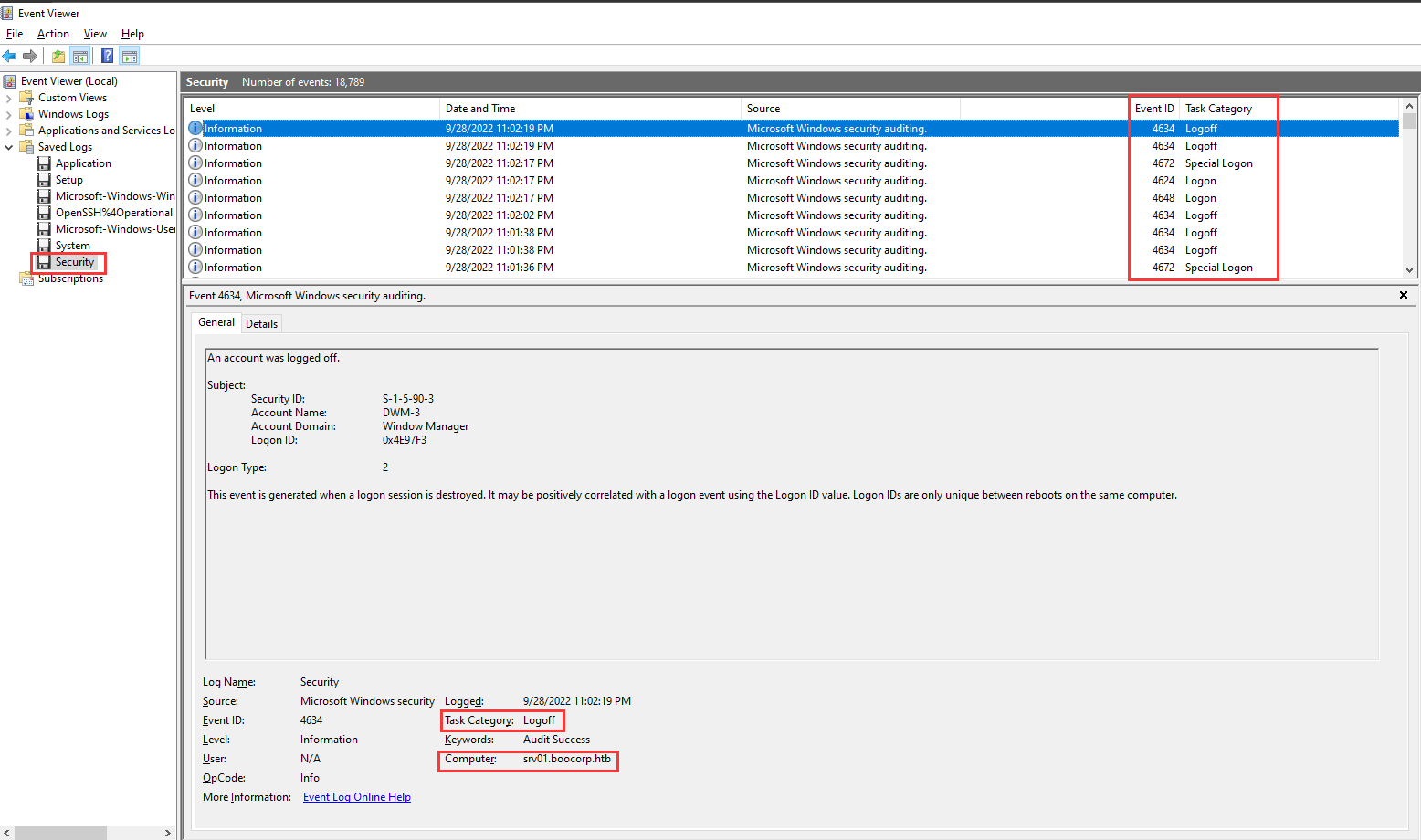
- Answer: Security
Which event log contains information about logon and logoff events? (for example: Setup)
> Security
[+] Correct!
Question 2
What is the event id for logs for a successful logon to a local computer? (for example: 1337)
>
- Answer: 4624
What is the event id for logs for a successful logon to a local computer? (for example: 1337)
> 4624
[+] Correct!
Question 3
Which is the default Active Directory authentication protocol? (for example: http)
>
- Answer: Kerberos
Which is the default Active Directory authentication protocol? (for example: http)
> Kerberos
[+] Correct!
Question 4
Looking at all the logon events, what is the AuthPackage that stands out as different from all the rest? (for example: http)
>
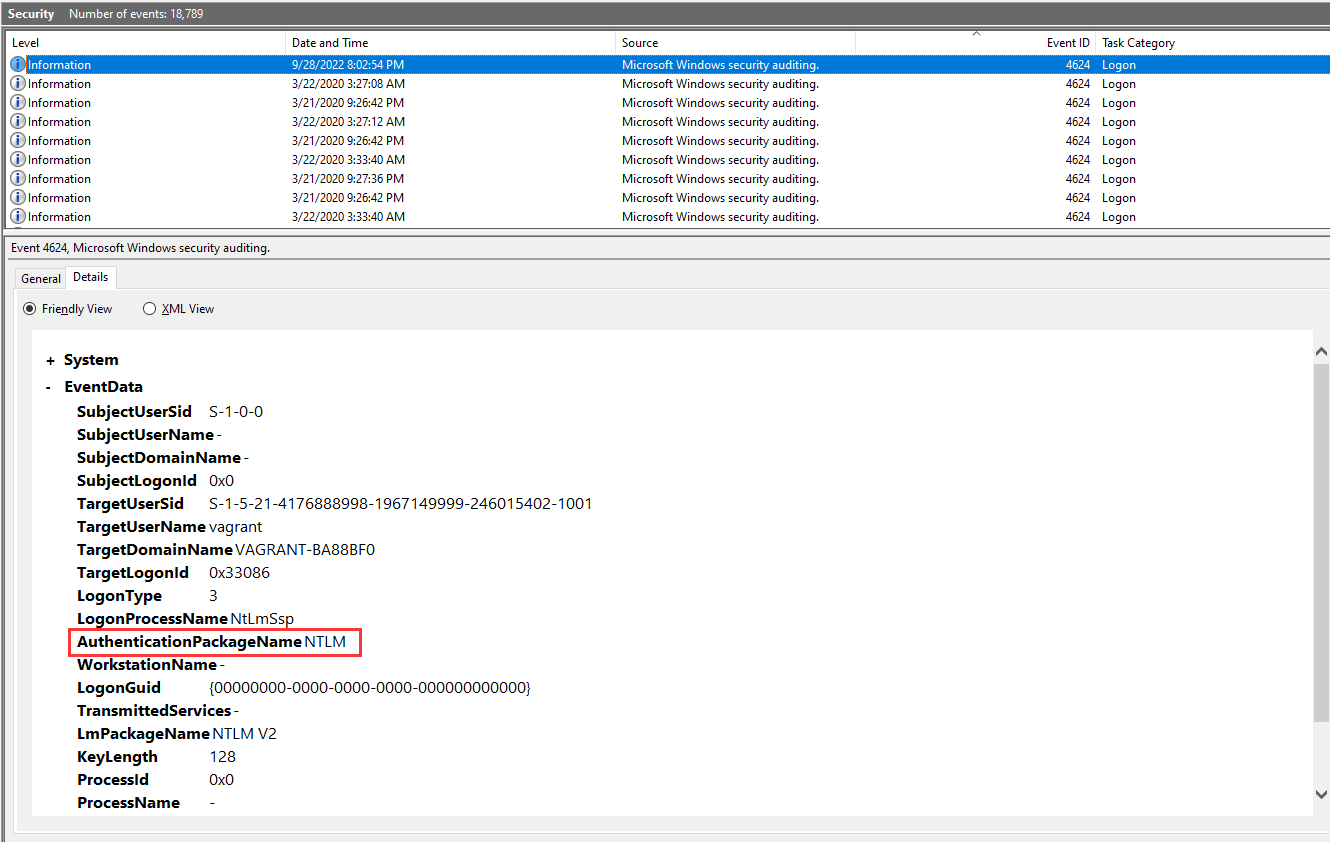
- Answer: NTLM
Looking at all the logon events, what is the AuthPackage that stands out as different from all the rest? (for example: http)
> NTLM
[+] Correct!
Question 5
What is the timestamp of the suspicious login (yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss) UTC? (for example, 2021-10-10T08:23:12)
>
After going through all the NTLM AuthPackage, I found 1 login log very sussy:
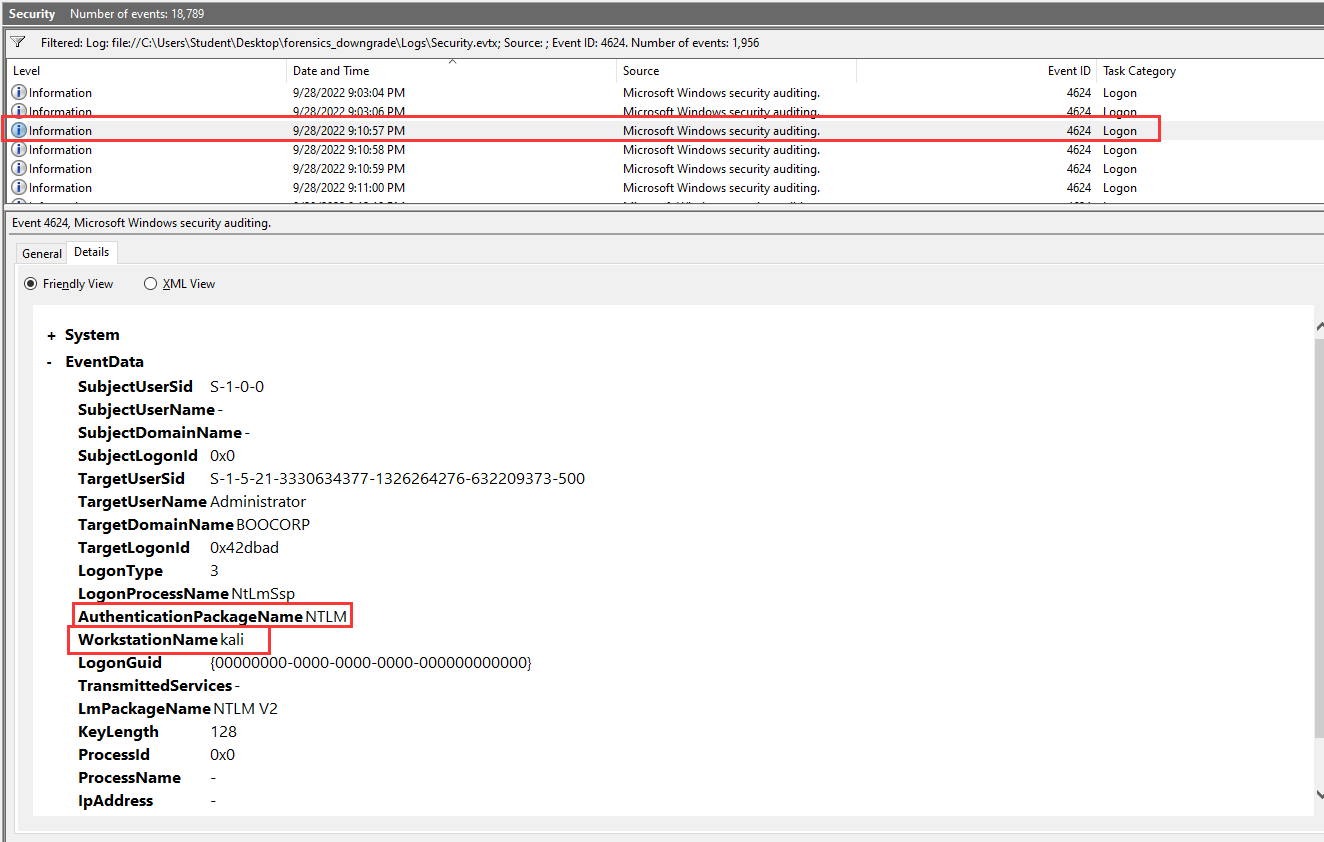
WorkstationName: kali
Hmm… This looks like is the attacker, let's grep the UTC timestamp:
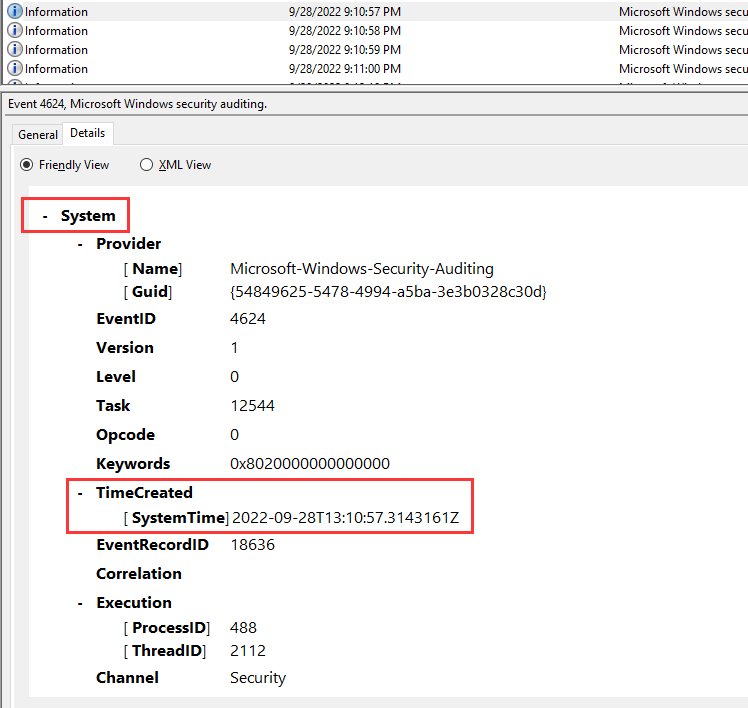
- Answer:
2022-09-28T13:10:57
What is the timestamp of the suspicious login (yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss) UTC? (for example, 2021-10-10T08:23:12)
> 2022-09-28T13:10:57
[+] Correct!
[+] Here is the flag: HTB{4n0th3r_d4y_4n0th3r_d0wngr4d3...}
We got the flag!
Conclusion
What we've learned:
- Windows Event Viewer Digital Forensics